Latest Updates
-
 Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner
Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner -
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause -
 Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft
Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft -
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet -
 What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions
What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions -
 Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles
Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles
Metabolic Syndrome: Its 5 Risk Factors, Causes, Treatment And Prevention
Metabolic syndrome is an umbrella term for a group of metabolic abnormalities such as insulin resistance, elevated blood pressure, diabetes, obesity and dyslipidemia. They are usually recognised to increase the risk of heart diseases, cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.

Metabolism is a chemical reaction that occurs inside the cells to produce energy from the food that we eat. Metabolic disorders occur when there's some disruption in the chemical reaction and the body is unable to use the food for energy production. There are multiple things which you should know about metabolic syndrome. Take a look.

Risk Factors Of Metabolic Syndrome
As aforementioned, metabolic syndrome (MS) is not a disease but a group of risk factors that lead to the condition. If a person has three or more of the following factors, there's an increased risk of MS. The risks include:
1. High triglyceride levels
Triglyceride is a type of lipid (fat) found in the blood. Whatever we eat, gets converted into calories. The extra calories which the body does not need during the time gets converted into triglycerides.
If a person keeps eating more and does fewers physical activities, high amount of triglycerides gets deposited in the blood vessels causing hardening, blocking or thickening of the artery walls. [1]
Normal level - Less than 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
High level - 200 to 499 mg/dL
2. Increased blood pressure
Hypertension or increased blood pressure is an important factor in metabolic syndrome. There are multiple factors that lead to hypertension development such as insulin resistance, oxidative stress, inflammation, sleep apnea and endothelial dysfunction. [2]
When triglycerides block the blood vessels, the blood is unable to flow efficiently throughout the body and causes pressure on the blood vessels. The heart has to pump the blood harder and in the process, leads to stroke or heart failure.
Normal: Less than 120 over 80 (120/80)
Hypertension crisis: Higher than 180/higher than 120
3. Increased fasting glucose
Fasting blood sugar gives vital information about how the body is managing blood sugar. High fasting glucose level indicates insulin resistance or diabetes. Glucose from the food gets converted into energy by a pancreatic hormone called insulin. It also helps in the storage of glucose for later use.
When a person consumes food, how high the glucose level rises depends on person' diet. If a person has insulin resistance, the body is unable to produce enough insulin or utilise insulin to break down the glucose into energy. This results in a high fasting glucose level.
According to a study, insulin resistance is associated with 2.8-fold increased risk of the first episode of stroke. [3]
Normal glucose level: 70 to 99 mg/dl
Prediabetes: 100 to 125 mg/dl
Diabetes: 126 mg/dl or above
4. Abdominal obesity
Abnormal obesity refers to the deposition of fat, especially around the abdomen. This is due to the dysfunction of adipose tissue. A study says that abdominal obesity is the predominant risk factor for MS. The study also predicts that around 50 per cent of the adults will be classified as obese by the year 2030 and MS will become a significant health problem.
The link between obesity and MS was described long back in 1991. However, it was also recognised that abdominal obesity does not always occur in people with high BMI. It can also occur in normal weighted metabolically obese people who have the excess deposition of fat in the waist area. [4]
Abdominal obesity in men: 40 inches or more waist size
Abdominal obesity in women: 35 inches or more waist size
5. Low levels of HDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is the good cholesterol in the body. It helps flush out the extra cholestrol and plaque from the arteries by sending them to the liver that helps in expelling those waste products out of the body. HDL keeps a check on your health level and decreases the risk of stroke and heart attack. [5]
The right choice of diet is good for maintaining a high level of HDL. The level of HDL decreases not with food but with conditions such as obesity, smoking, inflammation and diabetes.
In men: Less than 40 mg/dL
In women: Less than 50 mg/dL
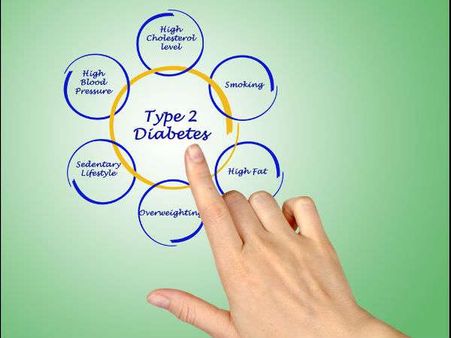
Causes Of Metabolic Syndrome
The exact cause of metabolic syndrome is not yet known. Out of the aforementioned points, insulin resistance is considered the main cause as it leads to high triglycerides levels which further leads to obesity, resulting in heart diseases. So, it's basically several risk factors acting together to cause MS.
Other causes include age and genetics which is not in our control. Controlling obesity and HDL levels by lifestyle changes may help to prevent MS but family history and age can play a major role sometimes.
Many researchesare still going on to know other conditions that cause MS such as PCOS, sleep apnea and fatty liver.

Symptoms Of Metabolic Syndrome
It includes all the symptoms of risk factors such as
- Large waist
- Diabetes (thirst, frequent urination and blurred vision)
- High blood pressure
- Low HDL levels
- High lipid profile

Diagnosis Of Metabolic Syndrome
- Medical history: To know about the existing conditions of a person such as diabetes. It also includes a physical examination of the patient like checking their waist size.
- Blood test: To check blood glucose levels.

Treatment Of Metabolic Syndrome
- Lifestyle change: People who are at an increased risk of MS are first instructed for lifestyle management to reduce the symptoms such as high glucose levels and high lipid profile. Doctors advise them to reduce weight through regular exercise and go on a healthy diet which is low in sugar, salt and fats. They also suggest quitting smoking.
- Medications: People who are at high-risk groups and who are not experiencing any changes after lifestyle modifications are suggested to take certain medication to control their glucose levels or high blood pressure.

How To Prevent
- Workout regularly. You can also consult a doctor for the type of exercise program.
- Recommend a DASH diet
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Cut down on saturated fats
- Quit smoking and alcohol
- Check your blood pressure and blood sugar level regularly

Common FAQs
1. What are the five signs of metabolic syndrome?
The five signs of metabolic syndrome include high blood glucose, high blood pressure, high lipid profile, large waist size and low HDL levels.
2. Can I reverse metabolic syndrome?
Yes, you can reverse metabolic syndrome with lifestyle changes such as exercise and proper diet. If you already have certain medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, lifestyle changes along with proper medications may do the work.
3. What foods should you avoid with metabolic syndrome?
People at higher risk of metabolic syndrome should avoid high fatty, refined and processed foods such as sugary drinks, pizza, white bread, fried food, pastries, pasta, cookies, potato chips, burger and sweetened cereals.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












