Latest Updates
-
 Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell
Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell -
 Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress
Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress -
 Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner
Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner -
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause -
 Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft
Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft -
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
Myths About HIV/AIDS You Should Not Believe
Listed here are a few of the myths associated with AIDS, check them out.
HIV/AIDS is often treated as a contagious disease in our society. It is believed that by sitting or sharing food with an HIV person, it exposes the risk of inviting this germ to our body. But the truth is not so.
There are some common myths about HIV that are still prevalent in our society, but as educated individuals, it is our duty to eradicate such beliefs, so that a HIV-infected patient can enjoy a healthy lifestyle.
HIV is a virus which when enters the human body affects the immune system of a person. If not treated in time, this can cause a severe damage to the immune system and make it incapable of fighting any disease.

AIDS, however, refers to symptoms and illnesses that can be seen at the final stage of HIV and if this is not treated, then the consequence can be fatal.
But before medical treatment, there are certain myths about HIV that need to be broken.
So, with the World AIDS Day just around, we have listed a few of the myths about HIV/AIDS that one needs to know of. They are as follows.

1. Sharing Foods With HIV/AIDS People:
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) cannot survive for a longer span when exposed to the environmental situation. But it is mostly believed that HIV can spread from one person to the next via sharing of food.
It is, however, a myth. HIV is a virus which is active only when it is inside the body but cannot survive outside. So keeping a HIV positive patient aloof from your group is an injustice to him/her. HIV patient is just a normal human being like all of us, but they require additional care because their immune system gets affected largely.
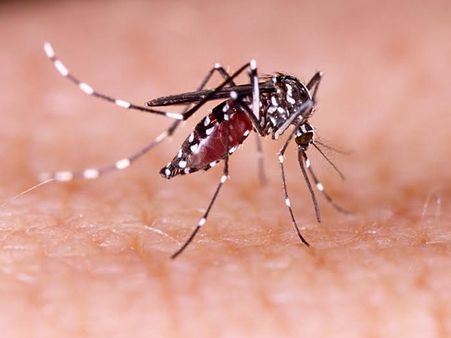
2. AIDS Spreads Through Mosquito Bites:
AIDS is the illness which occurs as a result of HIV in its final stage. And it is a wrong notion to believe that AIDS can occur from mosquito bites. This is because when a mosquito bites us, it sucks the blood from our vein. But it doesn't inject the blood of the last person (who might be affected by HIV). So, there is no chance of blood transfusion through which a person can get HIV from insect bites.

3. Only Sex Workers Get AIDS:
People often believe that only sex workers are prone to be infected with HIV. This is because they change their partner every day and are often engaged in unprotected sex. But if you are thinking so, then you are wrong. Yes, it is true that they too are highly prone to be infected with HIV, but that doesn't mean a normal couple is not in the danger zone.
HIV can occur to any person, and in most of the cases, an HIV patient doesn't realize the disease themselves. So, even if you are engaged in sexual activity with one partner, it is safe to use precautions, as it will further lower the risk of HIV, STD (sexually transmitted disease), and unwanted pregnancy.

4. HIV/AIDS Is Only Caused By Sex:
Another common belief about HIV is that it can be caused only by indulging in a sexual intercourse. Yes, unprotected sex is one of the modes to acquire HIV, but not the only one. HIV can be transmitted through a blood transfusion as well.
If an HIV infected person's blood is transferred to the body of a normal person, he/she is vulnerable to become a HIV patient. Apart from these, you can acquire HIV from an organ transplant, infected drugs or used needles, getting the blood of an HIV patient on any open wound like bruises or cuts in your body, and from mother to child during pregnancy or breastfeeding. So, there are ample ways to become vulnerable to this disease.

5. Baby Born To HIV Positive Mother Will Have The Infection:
Yes, it is seen that children get infected with HIV from their mother during pregnancy, birth, or while breastfeeding. But it is not mandatory that the child has to be infected. If he/she is born to a normal father and an HIV mother, they might not acquire the disease. However, such children are at a greater risk, so they should be checked thoroughly post their birth, and proper medical aid should be taken to prevent the virus from entering the child's body.
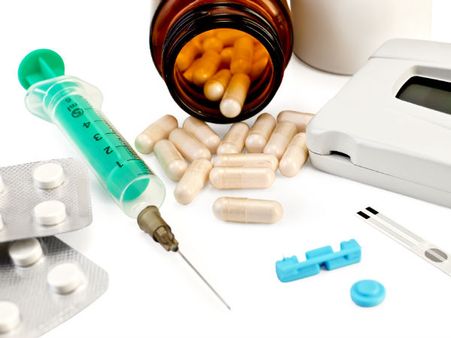
6. Keeping Off Medication For Sometime As They Are Powerful:
Once a person is detected with HIV, it is imperative to continue the medication as prescribed by the physician. But a few of us believe that, as these are strong medicines, these can eradicate HIV (just like a strong medicine can cure fever). But with HIV such is not the case. So, if you wish to live a healthy life, then it is essential to have proper medications and regular checkup at intervals.

7. Being Around HIV Positive People Spreads The Infection:
HIV is not contagious like flu or fever that by being with them, you will impose this deadly virus. The virus is active only in the human body and is very short-lived when comes in contact with the environment. So, by sharing food, hugging, kissing, moving around, etc., you are not prone to be affected by HIV. Also, by segregating an HIV patient, you are indirectly ill-treating that person and demoralizing his/her morale.

8. HIV/AIDS Positive Person Will Die Soon:
The most common myth about HIV/AIDS is that the lifespan of an HIV patient is short-termed. This is a wrong belief. With the advancement of science and technology, it is now seen that an HIV infected individual with the help of proper medication can live long and have a healthy family life as well. However, if it is not treated in time and it goes to the final stage of AIDS (which again if left untreated), then it can lead to death.
So, these are some of the myths about HIV which are widespread in our society. It is, therefore, our duty to create proper awareness about AIDS and prevent people from judging HIV patients based on such myths.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












