Latest Updates
-
 Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress
Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress -
 Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner
Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner -
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause -
 Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft
Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft -
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet -
 What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions
What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions
Osteomalacia: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis And Treatment
Osteomalacia is a disease which is characterized by the softening of the bones and it affects 1 in 1000 people globally. Don't confuse osteomalacia with the osteoporosis disease. Osteoporosis is the weakening of the bones and osteomalacia is softening of the bones.

What Causes Osteomalacia
Essential nutrients like calcium, phosphate, magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin D are required by the body to build strong bones. If the body is lacking in these nutrients, you tend to develop osteomalacia. It can also occur if the body is unable to absorb these minerals properly.
The most common problems that cause osteomalacia are:
- Vitamin D deficiency - Sunlight is the main source of vitamin D. People who live in areas where there isn't enough sunlight are at a higher risk of getting vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D deficiency is the most common cause of osteomalacia [1] .
- Kidney or liver problems - Both the kidney and liver are responsible for activating Vitamin D in the body. If there is any problem in the normal functioning of the kidney or liver, it can interfere with the body's ability to activate vitamin D [2] .
- Celiac disease - Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, which means eating gluten can cause sensitivity in people with this disease. Gluten triggers an immune response in the small intestine, which gradually damages the small intestine's lining and prevents it from absorbing some nutrients. This can lead to vitamin D and calcium deficiency [3] .
- Surgery - Certain surgeries are done to remove a part of your stomach and this can result in vitamin D and calcium deficiency. Because, intestines are the place where vitamin D, calcium and other nutrients are absorbed [4] .
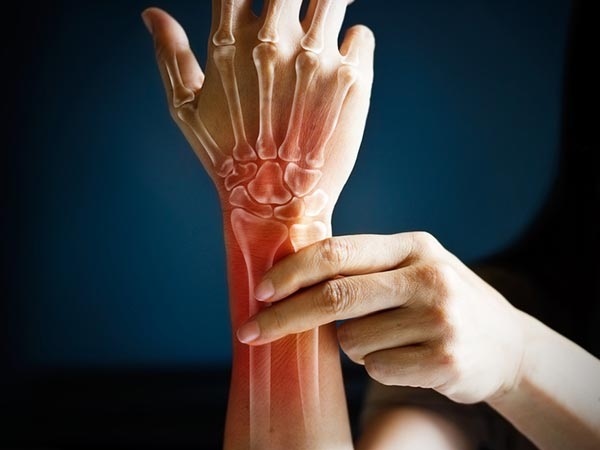
Symptoms Of Osteomalacia
When osteomalacia is in its early stages, you might not experience any symptoms. As osteomalacia progresses, you might have the following symptoms:
- Pain in the bone, especially in the hips.
- Dull, aching pain in the lower back, hips, legs, ribs and pelvis.
- Low levels of calcium can causes spasms in the hands and feet, numbness in the arms, legs and around your mouth, and irregular heart rhythms.

Risk Factors Of Osteomalacia [5]
- Under-exposure to sunlight.
- Full clothing that almost covers all the skin.
- People from the Indian sub-continent are at a risk of getting osteomalacia. It is because their skin doesn't absorb vitamin D well and their diet is lacking in vitamin D.
- Most people from the Indian sub-continent are lactose intolerant and this affects the absorption of calcium.
Complications Of Osteomalacia
People with osteomalacia are at a higher risk of breaking bones, particularly in the ribs, spine and legs.

Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Diagnosis Of Osteomalacia [6]
- Blood and urine tests - These tests will help detect whether your body has low levels of vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus.
- X-rays - An x-ray test will show small cracks in the bones.
- Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes test - This test will examine the levels of alkaline phosphatase, an enzyme produced by osteoblasts (the cells that form new bones). If alkaline phosphatase is at a high level, it means you have osteomalacia.
- Bone biopsy - A needle is inserted through skin into the pelvic bone above the hip to collect a small sample of the bone.
Treatment Of Osteomalacia [7]
- If the disease is caused by a lack of vitamin D, oral supplements of vitamin D are provided.
- If calcium and phosphate levels are low in the body, calcium and phosphate supplements are given.
- If osteomalacia is due to an underlying condition, the treatment procedure will start immediately.
Prevention Of Osteomalacia [8]
- Eat foods rich in vitamin D like oily fish, egg yolks, milk, yogurt, cereal, etc.
-
Eat foods rich in calcium like milk, yogurt, cheese, tofu, leafy greens, etc.
View Article References- [1] Noh, C. K., Lee, M. J., Kim, B. K., & Chung, Y. S. (2013). A case of nutritional osteomalacia in young adult male.Journal of bone metabolism,20(1), 51–55.
- [2] Dibble, J. B., & Losowsky, M. S. (1982). Osteomalacia in chronic liver disease.British medical journal (Clinical research ed.),285(6336), 157–158.
- [3] Tahiri, L., Azzouzi, H., Squalli, G., Abourazzak, F., & Harzy, T. (2014). Celiac disease causing severe osteomalacia: an association still present in Morocco!.The Pan African medical journal,19, 43.
- [4] Parfitt, A. M., Pødenphant, J., Villanueva, A. R., & Frame, B. (1985). Metabolic bone disease with and without osteomalacia after intestinal bypass surgery: a bone histomorphometric study.Bone,6(4), 211-220.
- [5] Mosekilde, L., & Melsen, F. (1976). Anticonvulsant osteomalacia determined by quantitative analysis of bone changes: Population study and possible risk factors.Acta Medica Scandinavica,199(1‐6), 349-356.
- [6] Bingham, C. T., & Fitzpatrick, L. A. (1993). Noninvasive testing in the diagnosis of osteomalacia.The American journal of medicine,95(5), 519-523.
- [7] Bhambri, R., Naik, V., Malhotra, N., Taneja, S., Rastogi, S., Ravishanker, U., & Mithal, A. (2006). Changes in bone mineral density following treatment of osteomalacia.Journal of Clinical Densitometry,9(1), 120-127.
- [8] Uday, S., & Högler, W. (2017). Nutritional Rickets and Osteomalacia in the Twenty-first Century: Revised Concepts, Public Health, and Prevention Strategies.Current osteoporosis reports,15(4), 293–302.
Comments



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












