Latest Updates
-
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet -
 What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions
What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions -
 Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles
Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles -
 Women’s Day 2026 Binge Watch: 10 Movies That Celebrate Women Who Challenge Norms And Rewrite Their Stories
Women’s Day 2026 Binge Watch: 10 Movies That Celebrate Women Who Challenge Norms And Rewrite Their Stories -
 Women’s Day 2026 Exclusive: Saumya Tandon On Dhurandhar Success, ‘Actors Must Break The Boxes’
Women’s Day 2026 Exclusive: Saumya Tandon On Dhurandhar Success, ‘Actors Must Break The Boxes’ -
 Rang Panchami 2026: Why This Colourful Post-Holi Festival Is Considered Auspicious For Married Couples
Rang Panchami 2026: Why This Colourful Post-Holi Festival Is Considered Auspicious For Married Couples
10 Risks Associated With Protein Overconsumption
Protein is a vital macronutrient that our body requires for growth and maintenance. It is the key to many biological processes in our body like promoting muscle growth, repairing tissues, making various hormones and boosting metabolism. Examples of animal-based proteins are meat, dairy products, fish and eggs while plant-based proteins are mainly grains, nuts, oats, quinoa, peanut butter and chia seeds.

No matter how important proteins are for our body, there are certain dietary limitations on their intake. Overconsumption of protein may increase the risk of stomach cancer, colon cancer, bone homeostasis, liver dysfunction and many more. Therefore, the daily intake of protein should not exceed the recommended amount as it may cause an adverse effect in the body.
Here are some of the risks associated with overconsumption of protein. Keep in mind all the risk factors and make your diet well balanced with protein.

1. Unwanted Weight Gain
A high-protein diet helps in weight loss but when a person overconsumes protein, it may cause unwanted weight gain. When the amount of protein exceeds in the diet, those excess protein gets stored in the form of fat resulting in weight gain. This happens because to consume more protein, we often end up consuming more calories. [1]

2. Constipation
Fibre is a type of carbohydrate which helps in the proper functioning of bowels and digestive system. When we consume more protein, the amount of fibre is restricted resulting in constipation. Consuming water along with fibre intake helps in bowel-related disorders. [2]
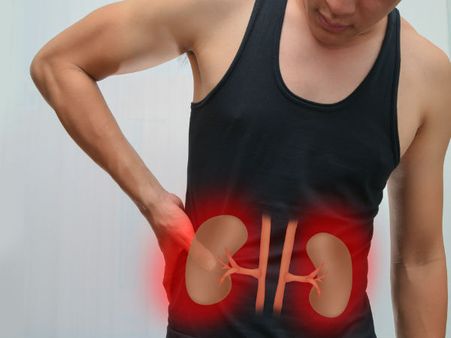
3. Renal Function Disorder
Overconsumption of protein increases acid loads in the kidney. Due to an increase in renal acid secretion, calcium kidney stones are formed. Excess intake of animal-based protein can also cause uric acid stone formation. Also, a decrease in the water level in the body along with excess protein consumption can make the condition worse. [2]

4. Dehydration
The excess amount of protein in our body increases the amount of nitrogen and amino acids. Our renal system has a certain capacity to metabolize and excrete nitrogen from our body. When the level of nitrogen exceeds the capacity, our body uses more water to get rid of it and in the process, dehydration occurs to prevent nitrogen build-up. [3]

5. Bad Breathe
High-protein diet makes our body go into a keto diet in which the body receives more calories from protein and fats rather than carbohydrates. Due to this, a substance called ‘ketone' is released by the liver which gets mixed with the blood, breathes and urine. Excess production of ketone due to the excess of protein causes bad breathe. [4]

6. Brain Fog
Eating an excess amount of protein might cause you to replace carbohydrates from the diet which are the main energy source for the proper functioning of the brain. This may lower down the learning, thinking and memory capabilities of the brain causing brain fog.

7. Diarrhoea
Choosing protein-rich foods all the time may cause you to neglect foods which are rich in fibres. Deficiency of fibre in our body affects the movement of bowels and digestive system. This often result in diarrhoea, especially if you also have lactose-intolerant. [2]

8. Risk Of Cancer
When animal-based protein foods like meat, poultry and seafood are cooked at high temperature, a chemical compound called heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) are formed as a result of the reaction between amino acids and creatine present in those protein sources. HAAs are usually a carcinogenic compound which may increase the risk of breast cancer, large-bowel cancer and colorectal cancer. [5]
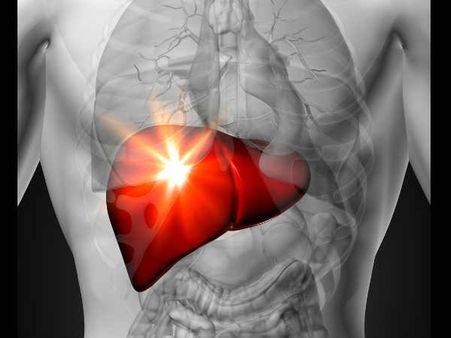
9. Liver Function Disorder
High protein diet can cause several disorders related to the liver. Inflammation or damage of the liver cells is often linked to increased protein diet. Individuals who consume high proteins have high levels of albumin and transaminases in the blood which are the indications of liver function disorder. This may cause symptoms like stomach pain.

10. Coronary Artery Disease
Excess amount of protein in the body is linked to inflammation and lipid deposition in the heart leading to coronary heart disease. Another study suggests that overconsumption of protein for a longer time increases the production of a gut-generated chemical called trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) which is responsible for heart diseases. [6]

Recommended Amount Of Protein
According to a study, the daily intake of protein for individuals are as follows:
- Healthy adult with less physical activity: 0.8 g- 1.0 g/kg body weight
- Healthy adults with moderate physical activity: 1.3 g/kg body weight
- Healthy adults with high physical activity: 1.6 g/kg body weight
Consumption of up to 2 g/kg body weight is considered safe for healthy adults. High dose of protein daily (greater than 2 g/kg body weight) can cause the aforementioned disorders. The recommended amount of protein intake for men is 55-57 g, and for women, it is 47-48 g. However, for athletes and pregnant women, the recommended amount of protein is slightly more than normal adults.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












