Latest Updates
-
 Holi 2026: The Aftercare Routine Your Skin And Hair Will Thank You For
Holi 2026: The Aftercare Routine Your Skin And Hair Will Thank You For -
 Over-Scrubbing After Holi? You Could Be Damaging Your Skin Microbiome, Not Just Removing Colour
Over-Scrubbing After Holi? You Could Be Damaging Your Skin Microbiome, Not Just Removing Colour -
 Horoscope for Today March 04, 2026 - Practical Steps for Calm Wins
Horoscope for Today March 04, 2026 - Practical Steps for Calm Wins -
 Happy Holi 2026 Wishes: 50+ Colourful Quotes, Messages, Status And Posts For WhatsApp, Facebook And Instagram
Happy Holi 2026 Wishes: 50+ Colourful Quotes, Messages, Status And Posts For WhatsApp, Facebook And Instagram -
 Lunar Eclipse 2026 Live: Last Total ‘Blood Moon’ Until 2028 — Check Sutak And Visibility
Lunar Eclipse 2026 Live: Last Total ‘Blood Moon’ Until 2028 — Check Sutak And Visibility -
 Holi 2026: Chef Sabyasachi Gorai Turns Festive Classics Into Gourmet Experiences
Holi 2026: Chef Sabyasachi Gorai Turns Festive Classics Into Gourmet Experiences -
 Holi 2026: Chef Ajay Chopra’s Hazelnut Kofta And Thandai Dessert Redefine Celebration
Holi 2026: Chef Ajay Chopra’s Hazelnut Kofta And Thandai Dessert Redefine Celebration -
 Holi 2026: 12 Incredible Ways Different States Celebrate the Festival of Colours
Holi 2026: 12 Incredible Ways Different States Celebrate the Festival of Colours -
 Lunar Eclipse 2026: Health, Food, And Pregnancy Myths Debunked
Lunar Eclipse 2026: Health, Food, And Pregnancy Myths Debunked -
 Holi 2026: Are ‘Herbal’ Holi Colours Really Safer? Expert Explains The Safety Gap
Holi 2026: Are ‘Herbal’ Holi Colours Really Safer? Expert Explains The Safety Gap
Diabetes Awareness Month 2019: 24 Foods That Help Manage Diabetes
Every year, the month of November is observed as the Diabetes Awareness Month - celebrated globally to raise awareness about both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. The theme of World Diabetes Day and diabetes awareness month 2019 is 'Family and Diabetes'.
Diabetes Awareness Month 2019 also aims to focus on the link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease. On this awareness month, let us take a look at the different types of food that can help manage the condition.
Diabetes is a chronic disorder that needs to be treated effectively. Yet the best treatment for this chronic disease is its prevention. It is possible to forestall diabetic health complications by keeping the disease under control. In severe cases, diabetes can develop major health complications such as stroke or kidney disease. Some main symptoms of diabetes are increased thirst and hunger, weight loss, fatigue, tiredness, increased urination, slow healing of wounds [1] .
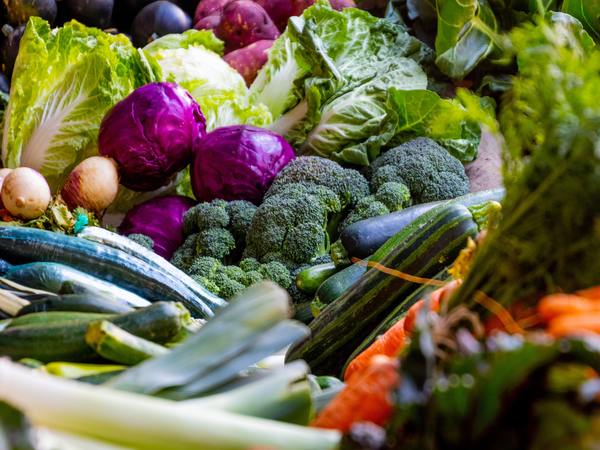

Known to be a disease with multifactorial aetiology, diabetes requires various solutions to manage the condition, be it by taking pills, following a stringent diet and making lifestyle changes. The most important strategy to prevent diabetes is to identify the presence of risk factors as well as to focus on dietary guidelines. Eating foods that are high in fibre such as fruits, vegetables, beans, whole grains and nuts can trim down the risk of diabetes [2] .
The amount and the type of sugar are the main factors that help in categorizing foods into best and worst. If you are diabetic, you have to look at the glycaemic index (GI) of all food items, apart from the nutrient content [3] . Prefer foods with a low glycaemic index and avoid those with a high glycaemic index.
Foods That Help Manage Diabetes
1. Fenugreek
The leaves and seeds are extremely beneficial for stabilising the blood sugar levels in your body. Several herbs have been used to aid with the signs and symptoms of diabetes. Among the more prevalent ones, fenugreek helps in keeping the levels of blood sugar stable, enhances glucose tolerance and assists in glucose excretion [4] .
2. Cayenne pepper
Possessing antidiabetic effects, cayenne peppers help reduce the glucose level in your blood by increasing the insulin levels and glycogen content. The capsaicin compound in the peppers is responsible for lowering your blood pressure [5] .

3. Cinnamon
One of the most common kitchen ingredients, cinnamon has shown effective results in lowering the blood sugar level and improving insulin sensitivity. It has antioxidant properties, which can also lower the triglyceride levels in type 2 diabetes and cholesterol [6] . If consumed for a period of 3 months, cinnamon can control the haemoglobin A1c, which determines the level of long-term diabetes. It also aids the type-1 diabetes level, but one must limit its consumption to 1 teaspoon daily [7] .
4. Egg
A rich source of protein, consuming eggs can help improve the insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation and increase the good HDL cholesterol and decrease the bad LDL cholesterol. Hard-boiled eggs help cut down the blood sugar levels [8] .
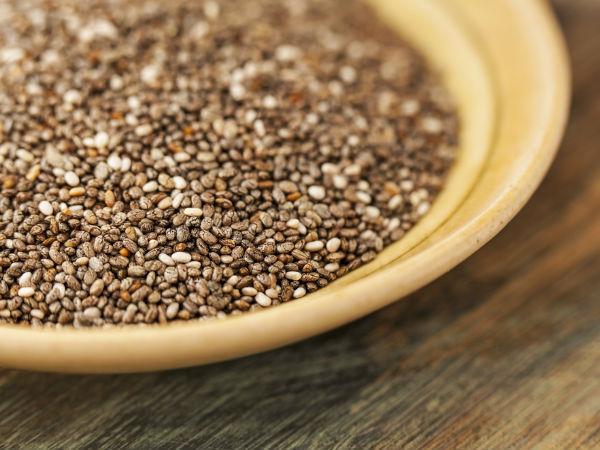
5. Chia seeds
The low amount of digestible carbohydrates and the rich source of fibre help maintain a healthy balance in the blood sugar level. The chia seeds reduce the speed at which the food consumed moves through the gut and gets absorbed in the body [9] . Chia seeds are beneficial in preventing and treating diabetes, as these enable insulin regulation.

6. Greek yoghurt
Apart from being a good source of gut-healthy bacteria, yoghurt is a good choice for those people with diabetes. In order to control the blood sugar level and reduce the risk of developing heart disease, consuming Greek yoghurt can be beneficial due to its probiotics content. This dairy product not only helps in weight loss but improves the body composition of type 2 diabetic people as well [10] .
7. Turmeric
Curcumin, an active ingredient in turmeric, helps in lowering the blood sugar, inflammation, and decreases the potential chance of having a heart ailment. It also improves kidney health which gets worst affected in case of diabetes [11] .
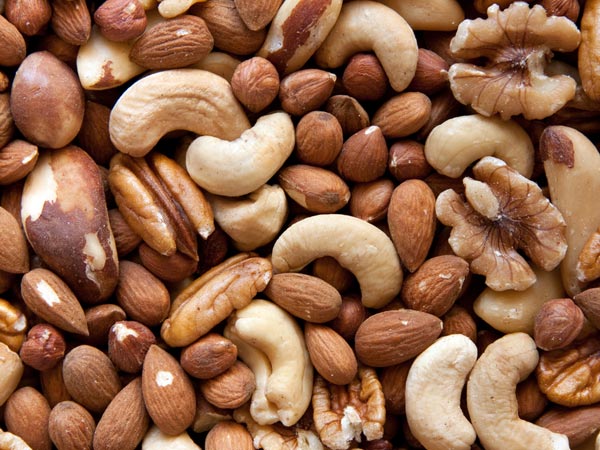
8. Nuts
Hazelnuts, almonds, pecans, Brazil nuts, pistachios, cashews, Macadamia nuts, and walnuts are a rich source of fibre and contain low digestible carbohydrates. Studies reveal that daily consumption of these nuts can help in controlling the blood sugar level and reduce inflammation, LDL cholesterol level, and insulin level [12] .

9. Broccoli
Extremely beneficial for type 2 diabetes, consuming broccoli can help prevent dangerous blood sugar spikes [13] . Also, other green vegetables such as lettuce, cabbage, spinach, parsley, celery, cucumber, cauliflower, green beans and kohlrabi help improve insulin sensitivity and thus better regulate blood glucose levels. Eating these vegetables can help in cases of diabetes and obesity, and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes because vegetables are rich in magnesium and are known as effective antioxidants [14] .
10. Flax seeds
In order to control the blood sugar level and improve the heart health, consumption of flax seeds is a healthy option. People who are suffering from type 2 diabetes have shown an increase in the haemoglobin A1c level after consuming flax seeds for 12 weeks [15] . The high-viscous fibre helps in improving the gut health, reducing the risk of heart attack and strokes, preventing the occurrence of blood clots, increasing insulin sensitivity, and satiating the hunger pangs for a long span [12] .
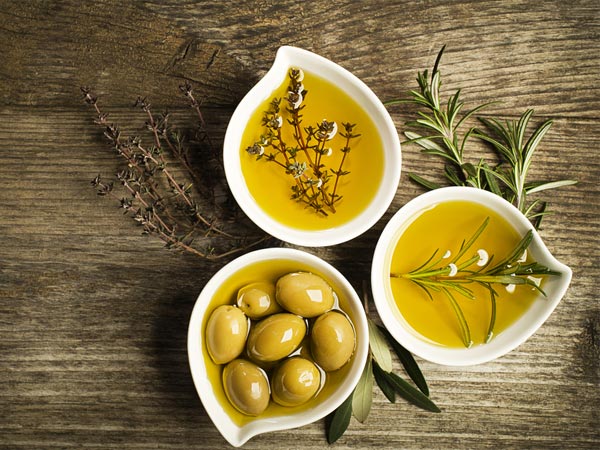
11. Extra-virgin olive oil
A rich source of oleic acid, extra-virgin olive oil helps in escalating the HDL cholesterol level and triglycerides level for the type 2 diabetes patients [11] . Consumption of this oil has shown an increase in the GLP-1 hormone and reduced the risk of heart disease.

12. Apple cider vinegar
To improve insulin sensitivity and lower the fasting blood sugar level, consuming apple cider vinegar is the best option. When consumed with a carbohydrate enriched meal, apple cider vinegar can reduce nearly 20 per cent of the blood sugar level. Consuming two tablespoons of this vinegar during bedtime can lead to a 6 per cent reduction in the blood sugar level [15] .
13. Strawberries
Enriched with antioxidant anthocyanins, strawberries are one of the most nutritious fruits that one can eat. This antioxidant helps in reducing the insulin level after the meal and controls the blood sugar level for type 2 diabetes patients. Blueberries are also beneficial in managing diabetes [16] .
14. Garlic
A herb with immense nutritional benefits, garlic not only enhances the taste of the food but controls the blood sugar level, inflammation, and LDL cholesterol for type 2 diabetes patients as well. Consuming a clove of garlic every day can also help in reducing the blood pressure level [17] .
15. Shirataki Noodles
The noodles contain a high amount of glucomannan fibre that is extracted from the roots of Konjac. Its medicinal benefits render a lower level of blood sugar and improve health by eliminating the factors that can trigger diabetes [9] .

16. Beans
People with diabetes should consume dried beans and avoid the sodium content of canned beans. Beans, which are low in the glycaemic index, help repress the blood sugar levels better than any other starchy foods [17] .
17. Brown rice
White rice can get your blood sugars soaring, so make sure to replace it with brown rice. Consuming brown rice reduces diabetes risk by almost 15 per cent. Moreover, replacing rice with other grains can reduce or prevent diabetes by 35 per cent [18] .

18. Asparagus
By controlling your blood sugar levels, this green vegetable can help boost the output of insulin, which can eventually make the body to sop up glucose. Regular consumption of asparagus has a considerable effect on keeping the blood sugar levels under control as well as the body's production of insulin [19] .
19. Apple
There is no denying that fruits like apples, blueberries and grapes are healthy and an essential part of the diet for everyone. These fruits are linked to reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes if consumed frequently. People who eat apples every day can lower their risk of type 2 diabetes by 27 per cent than those who don't eat apples [15] .
20. Barley
It has soluble fibre and prevents diabetes by rapidly improving people's health. Not many people are aware that barley is excellent in steadying your blood sugar levels and lowering cholesterol by 6 per cent. Barley is rich in soluble fibre called beta-glucan. Beta-glucan lowers the LDL cholesterol and manages to stall your body's ability to absorb it [11] .

21. Oats
A simple home remedy for sugar control is to start your day with oats. Oats contain a high percentage of fibre, B vitamins (especially B1), vitamin E and antioxidants. A large amount of fibre in oats causes slower absorption of glucose and help stabilize blood sugar levels, making it one of the best foods for diabetes [18] .
22. Dark chocolate
Researchers found that dark chocolate improves cell sensitivity to insulin and significantly improves the chances of avoiding diabetes. In addition, dark chocolate lowers blood pressure and the amount of bad cholesterol in the body. It also helps strengthen your blood vessels [20] .
23. Green tea
Having green tea is an effective way to control diabetes [21] . Green tea contains the antioxidant EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate), which helps to maintain the flexibility of blood vessels and stabilizing blood glucose levels. A recent study found that this element reduces blood sugar levels and prevents its sharp rise after a meal consisting mainly of carbohydrates.
24. Fish
The omega-3 fatty acids present in fish is good for diabetics as they help to reduce the insulin resistance in the body [22] .

Apart from the above-mentioned varieties of food, tomatoes, carrots, multi-grain bread, citrus fruits, beef, peanut butter, avocado, guava, Indian dal, bottle gourd, okra, bitter gourd, gram flour, and pumpkin seeds are also beneficial for managing diabetes.
Sample Indian Meal Plan For Diabetes
Sunday
Breakfast: Baked vegetable cutlet or 1 egg with 1-2 whole wheat toast with grilled vegetables and a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk [23] .
Lunch: 1-2 cups of brown rice, vegetables, salad and 1 bowl of chana or chicken or whole wheat pasta with vegetables and salad.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with mixed vegetables and salad along with 1 bowl of dal.
You can have fruits or roasted chana as snacks.

Monday
Breakfast: Vegetable stuffed chapati or 1 egg with 1-2 whole wheat toast with grilled vegetables and a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 1-2 barley chapatis with vegetables, 1 bowl of dal and curd.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with vegetables and salad along with 1 bowl of dal or curd.
Tuesday
Breakfast: Vegetable oats or 2- egg whites or 2- egg whites with 1-2 whole wheat toast with grilled vegetables along with a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 2 dal chapatis and vegetable salad and curd.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with mixed vegetables and salad along with 1 bowl of fish or dal.
Wednesday
Breakfast: Milk with oats or 2 egg whites with 1-2 whole wheat toast with grilled vegetables along with a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 1-2 chapatis with vegetable salad and low-fat paneer or chicken.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with vegetable and salad along with 1 bowl of fish or dal.
Thursday
Breakfast: Idli, poha or upma with vegetables along with a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 1-2 chapatis with vegetable salad and low-fat paneer or curd.
Dinner: 1-2 besan cheela (chilla) or oats with vegetables and salad along with 1 bowl of fish or dal.
Friday
Breakfast: Whole wheat sandwich or chicken sandwich along with a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 1-2 chapatis with mixed vegetables, salad and low-fat paneer or 1 bowl of curd.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with mixed vegetables and salad along with 1 bowl of fish or dal.
Saturday
Breakfast: Moong dal cheela (chilla) with vegetables or stuffed multi-grain chapati with a cup of tea or coffee or low-fat milk.
Lunch: 1-2 chapatis, vegetables, salad and 1 bowl of sprout or 2 egg white curry.
Dinner: 1-2 chapatis with vegetables and salad along with curd or dal.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- [1] Nabors, L., Troillett, A., Nash, T., & Masiulis, B. (2005). School nurse perceptions of barriers and supports for children with diabetes.Journal of School Health,75(4), 119-124.
- [2] Hill, J. O., & Peters, J. C. (2002). Biomarkers and functional foods for obesity and diabetes.British Journal of Nutrition,88(S2), S213-S218.
- [3] Hu, J., Amirehsani, K., Wallace, D. C., & Letvak, S. (2013). Perceptions of barriers in managing diabetes: perspectives of Hispanic immigrant patients and family members.The Diabetes Educator,39(4), 494-503.
- [4] Rubin, R. R., & Peyrot, M. (2001). Psychological issues and treatments for people with diabetes.Journal of clinical psychology,57(4), 457-478.
- [5] Leach, M. J., & Kumar, S. (2012). Cinnamon for diabetes mellitus.Cochrane database of systematic reviews, (9).
- [6] Watcharachaisoponsiri, T., Sornchan, P., Charoenkiatkul, S., & Suttisansanee, U. (2016). The α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activity from different chili pepper extracts.International Food Research Journal,23(4).
- [7] Tamez, M., Virtanen, J. K., & Lajous, M. (2016). Egg consumption and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a dose–response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.British Journal of Nutrition,115(12), 2212-2218.
- [8] Vuksan, V., Jenkins, A. L., Brissette, C., Choleva, L., Jovanovski, E., Gibbs, A. L., ... & Duvnjak, L. (2017). Salba-chia (Salvia hispanica L.) in the treatment of overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind randomized controlled trial.Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases,27(2), 138-146.
- [9] Udovicki, B., Djekic, I., Kalogianni, E. P., & Rajkovic, A. (2019). Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization of Aflatoxin M1 Intake through Consumption of Milk and Yoghurt by Student Population in Serbia and Greece.Toxins,11(4), 205.
- [10] Adab, Z., Eghtesadi, S., Vafa, M. R., Heydari, I., Shojaii, A., Haqqani, H., ... & Eghtesadi, M. (2019). Effect of turmeric on glycemic status, lipid profile, hs‐CRP, and total antioxidant capacity in hyperlipidemic type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.Phytotherapy Research.
- [11] Lenoir-Wijnkoop, I., Mahon, J., Claxton, L., Wooding, A., Prentice, A., & Finer, N. (2016). An economic model for the use of yoghurt in type 2 diabetes risk reduction in the UK.BMC Nutrition,2(1), 77.
- [12] Hernández-Alonso, P., Camacho-Barcia, L., Bulló, M., & Salas-Salvadó, J. (2017). Nuts and dried fruits: An update of their beneficial effects on type 2 diabetes.Nutrients,9(7), 673.
- [13] Holmes, D. (2017). Diabetes: Could broccoli have a role in combating type 2 diabetes mellitus?.Nature Reviews Endocrinology,13(8), 437.
- [14] Suresh, S., Waly, M. I., Guizani, N., & Rahman, M. S. (2016). Broccoli (Brassica oleracea) extract combats Streptozotocin-induced diabetes and oxidative stress in rats.The FASEB Journal,30(1_supplement), 404-6.
- [15] Sweazea, K. L., & Johnston, C. S. (2019). Cardioprotective Potential of Flaxseeds in Diabetes. InBioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Diabetes(pp. 361-374). Academic Press.
- [16] Bozzetto, L., Alderisio, A., Giorgini, M., Barone, F., Giacco, A., Riccardi, G., ... & Annuzzi, G. (2016). Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Reduces Glycemic Response to a High–Glycemic Index Meal in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Diabetes Care,39(4), 518-524.
- [17] Roy, N., Nazeem, P. A., & Abida, P. S. (2017). Comparative docking studies to prove the accuracy of computational tools for recognizing the inhibitory action of garlic (Allium sativum L.) on diabetes.IJCS,5(4), 342-345.
- [18] Kondo, K., Morino, K., Nishio, Y., Ishikado, A., Arima, H., Nakao, K., ... & Suwa, M. (2017). Fiber-rich diet with brown rice improves endothelial function in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial.PloS one,12(6), e0179869.
- [19] Wesam, E. M., Yakout, A., Samy, A. A., & Souad, A. A. (2018). ANTIDIABETIC AND KIDNEY PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF ASPARAGUS RACEMOSUS IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETES IN RATS.
- [20] Greenberg, J. A. (2015). Chocolate intake and diabetes risk.Clinical nutrition,34(1), 129-133.
- [21] Yu, J., Song, P., Perry, R., Penfold, C., & Cooper, A. R. (2017). The effectiveness of green tea or green tea extract on insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis.Diabetes & metabolism journal,41(4), 251-262.
- [22] Turyk, M., Fantuzzi, G., Persky, V., Freels, S., Lambertino, A., Pini, M., ... & Anderson, H. A. (2015). Persistent organic pollutants and biomarkers of diabetes risk in a cohort of Great Lakes sport caught fish consumers.Environmental research,140, 335-344.
- [23] Times Now. (2019, Aoril 16). 7-day Indian diet plan for type 2 diabetes: Vegetarian and non-vegetarian food chart to control blood sugar [Blog post]. Retrieved from, https://www.timesnownews.com/health/article/7-day-indian-diet-plan-for-type-2-diabetes-best-diabetic-meal-plan-to-control-blood-sugar-and-aid-weight-loss/400870



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












