Latest Updates
-
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause -
 Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft
Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft -
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet -
 What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions
What If WiFi, GPS Or Dishwashers Didn’t Exist? This Instagram Reel Credits Women Behind Everyday Inventions -
 Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles
Women’s Day 2026: Why Creating Relaxation Spaces At Home Matters For Women Balancing Multiple Roles -
 Women’s Day 2026 Binge Watch: 10 Movies That Celebrate Women Who Challenge Norms And Rewrite Their Stories
Women’s Day 2026 Binge Watch: 10 Movies That Celebrate Women Who Challenge Norms And Rewrite Their Stories
Thyromegaly: Everything You Need To Know
A condition wherein the butterfly-shaped gland in the neck turns abnormally large is known as thyromegaly. We commonly refer to this condition as goitre. Although the major reason behind it is insufficient iodine, there could be other causes associated with its occurrence as well. Roughly, one-third of the world's population suffers from a low iodine intake.

The severity of the situation is high in case of people who live far away from the ocean areas (or at higher elevations) as it has been found that such people do not get enough iodine intake through their diet. When the thyroid gland can't make enough hormone, it enlarges in order to compensate.
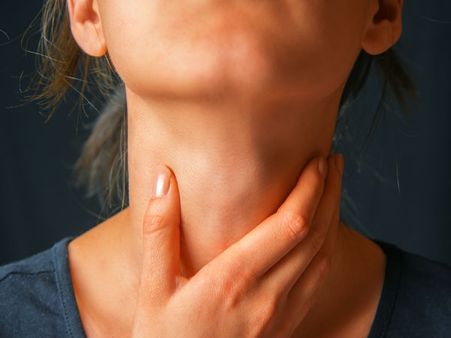
What Is Thyromegaly?
When a person has goitre, the enlarged, swollen gland is quite visible from the outside of the neck. A person with this condition finds it difficult to swallow and breathe. In case the condition is left untreated, it can cause serious harm wherein the thyroid gland can turn highly ineffective and stop making thyroid hormone at all or making too much of it leading to hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism respectively.
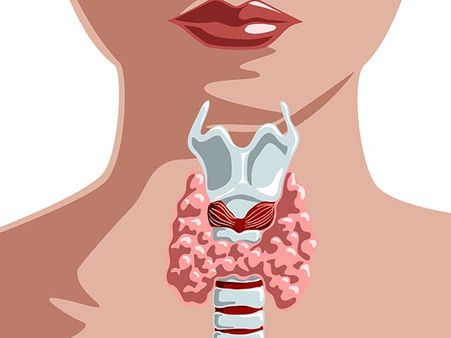
Different types of thyromegaly
Based on the thyroid's functionality, size and growth pattern, the different types of thyromegaly are:
- Euthyroid - Swelling does not affect the normal functioning of the gland
- Hyperthyroidism - Thyroid gland becomes overactive
- Hypothyroidism - Thyroid produces less than the normal amounts of thyroid hormone
- Diffuse goitre - Enlargement of the gland is due to hyperplasia
- Nodular goitre - Raised areas of tissues within the thyroid causing swelling
- Cystic goitre - Thyroid nodules filled with fluid
- Class 1 - Swelling normally not externally visible
- Class 2 - Swelling can be seen and felt
- Class 3 - Swelling is large and extends towards the sternum

What Are The Causes Of Thyromegaly?
The primary causes of this condition are:
- Iodine deficiency: The prime contributor to the production of T4 and T3 hormones is iodine. When thyroid cannot make enough hormone, as a compensation, it enlarges.
- Graves' disease: This is an autoimmune disease. The immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. In a course of events, the thyroid begins to overstimulate and produce excess hormones.
- Hashimoto's disease: This is an autoimmune disorder. Thyroid gland is damaged and is unable to produce enough hormone.
- Nodules: This happens when the fluid-filled nodules grow on the gland and make the gland large.
- Inflammation: Inflammation of the gland is called thyroiditis. It can be caused due to an infection, radiation therapy or medication.

What Are The Early Signs And Symptoms?
The primary symptom is an enlarged thyroid gland. It might be visible externally from the outside of the neck. Due to the pressure of the enlarged area, the following symptoms might occur:
- Coughing
- Tightness in the neck
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty in breathing or swallowing

Symptoms associated with hypothyroidism:
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Stiff joints
- Weakness
- Dry hair and skin
- Constipation
- Weight gain

Symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism:
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Brittle hair
- Increased appetite
- Irregular heartbeat
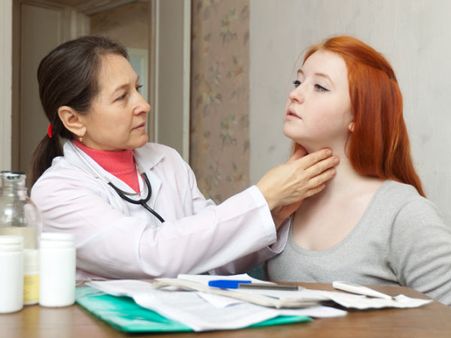
How Is Thyromegaly Diagnosed?
A physical examination of the neck can help a doctor diagnose the presence of thyromegaly. The routine physical examination would involve the doctor feeling around the neck and would ask you to swallow. The underlying cause might need to be identified in case an enlarged gland is found.
The following may be done to diagnose the underlying cause:
- Thyroid hormone tests: This involves measuring the amount of TSH and T4 through a blood test.
- Ultrasound: This would create an image of the thyroid gland to help the doctor assess the condition.
- Thyroid scan: A radioactive isotope is injected in a vein located on the inside of your elbow. This produces an image of the thyroid on a computer screen which the doctor can assess.
- Biopsy: A sample of the tissue from the thyroid is taken using a fine needle and sent to the laboratory for tests.
- Antibody tests can also help the doctor assess your thyromegaly condition.

What Are The Treatment Options?
The symptoms of thyromegaly are treated and it ideally depends on the underlying cause.
- Due to iodine deficiency: Small doses of iodine can help in shrinking the thyroid gland.
- Due to Hashimoto's disease: This is usually treated using synthetic thyroid hormone replacement.
- Due to Graves' disease: Medication would help lower the production of thyroid hormones.
- During pregnancy: Thyromegaly during pregnancy can cause issues such as premature birth and low birth weight. Pregnant women are prescribed medication to treat an overactive thyroid gland. Radioiodine therapy is not recommended during pregnancy.
- Due to nodules: Nodules that are not cancerous are not treated, however, one would require close monitoring over the years. Synthetic thyroid hormones are prescribed in case the nodule overproduces thyroid hormones.
- Due to inflammation: Mild anti-inflammatory medicines can help in reducing pain. Oral steroids might be prescribed in case the swelling is severe.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












