Just In
- 3 hrs ago

- 3 hrs ago

- 7 hrs ago

- 14 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Movies
 Pukaar Dil Se Dil Tak Promo: Sayli Salunkhe Impresses In First Video Of Sony TV Show, Details About Her Role
Pukaar Dil Se Dil Tak Promo: Sayli Salunkhe Impresses In First Video Of Sony TV Show, Details About Her Role - Sports
 Who Won Yesterday's IPL Match 34? LSG vs CSK, IPL 2024 on April 19: KL Rahul Stellar Batting Show Decimate Chennai Bowling
Who Won Yesterday's IPL Match 34? LSG vs CSK, IPL 2024 on April 19: KL Rahul Stellar Batting Show Decimate Chennai Bowling - Finance
 Rs 17/Share Dividend: Record Date On April 26; Buy The ICICI Group Stock To Be Eligible?
Rs 17/Share Dividend: Record Date On April 26; Buy The ICICI Group Stock To Be Eligible? - News
 Chinese President Xi Jinping Orders Biggest Military Reorganisation Since 2015
Chinese President Xi Jinping Orders Biggest Military Reorganisation Since 2015 - Education
 Exam Pressure Does Not Exist; Studying Punctually is Crucial; Says Aditi, the PSEB 2024 Topper
Exam Pressure Does Not Exist; Studying Punctually is Crucial; Says Aditi, the PSEB 2024 Topper - Automobiles
 Suzuki Swift Hatchback Scores 4 Star Safety Rating At JNCAP – ADAS, New Engine & More
Suzuki Swift Hatchback Scores 4 Star Safety Rating At JNCAP – ADAS, New Engine & More - Technology
 Dell Introduces AI-Powered Laptops and Mobile Workstations for Enterprises in India
Dell Introduces AI-Powered Laptops and Mobile Workstations for Enterprises in India - Travel
 Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions
Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions
Lupus: What Causes This Autoimmune Condition? Types, Symptoms, Complications And Treatment
Known as the "disease of a thousand faces," lupus is an autoimmune disorder that damages healthy tissues over time. Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease which can cause joint pain, fever, skin rashes, and organ damage. It is most commonly seen in women - typically between the ages of 15 and 45 [1].

Types Of Lupus
There are several different kinds of lupus, such as the following [2][3]:
1. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): A majority of lupus cases are classified as SLE, which constitutes 70 per cent of all cases. The symptoms of SLE may range from mild to severe, and it is a systemic condition. Therefore, it may affect multiple organs and systems throughout the body. Because of this, SLE tends to be a more severe form of lupus.
2. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE): DLE is a type of cutaneous lupus that causes lesions on the skin. Typically, these lesions appear on the scalp and face, although they can also affect other body parts, such as the ears. A person with DLE does not suffer from internal organ damage, but around 10 per cent of people with DLE develop SLE as a result of the disease.
3. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE): The term acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus refers to skin lesions that appear on parts of the body exposed to sunlight, causing discolouration of the skin rather than scarring.
4. Neonatal lupus: During pregnancy, certain antibodies are passed through the placenta from the mother to the infant, which causes neonatal lupus in the infant.
5. Drug-induced lupus (DIL): DIL is an autoimmune condition that certain medications can cause. Its symptoms are similar to SLE, but it is usually less severe. Over 100 trusted source medications have been identified as potential causes of DIL.

What Causes Lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune condition; however, the cause is unknown. When a person suffers from an autoimmune condition, such as Lupus, their immune system is unable to distinguish between foreign substances and healthy tissue. This is why the body mistakenly perceives itself as foreign [4].
Consequently,
the
immune
system
directs
antibodies
against
both
healthy
tissues
and
antigens,
resulting
in
swelling,
pain,
and
tissue
damage.
It
is
common
for
people
with
autoimmune
diseases,
such
as
lupus,
to
develop
antinuclear
antibodies.
These
antibodies
target
the
nucleus
of
the
body's
own
cells,
which
contains
the
genetic
material.
Drug-induced
lupus
can
be
caused
by
drugs
such
as
hydralazine
(a
hypertension
medication),
procainamide
(a
heart
arrhythmia
medication),
isoniazid
(an
antibiotic
used
to
treat
tuberculosis),
and
minocycline
(an
antibiotic
used
to
treat
some
skin
conditions)
[5].
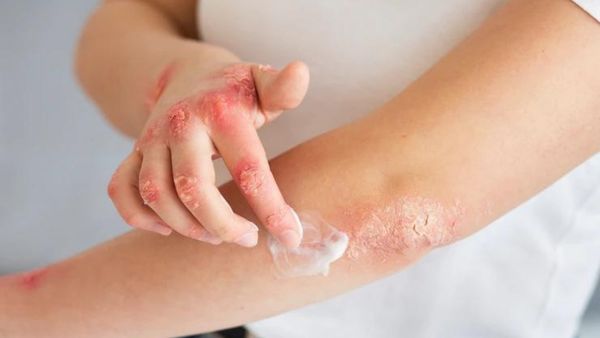
What Are The Symptoms Of Lupus?
Lupus has a wide range of symptoms, such as the following [6]:
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint pain
- Fever
- Chest pain when breathing deeply
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Mouth ulcers
- Memory problems
- Headaches
- Unusual hair loss
- Malar rash, a red, butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks
- Pale or purple fingers or toes from cold or stress, known as Raynaud's disease
- Arthritis
- Hair loss
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Mouth ulcers
- Arthritis
- Malar rash
- Cardiovascular complications
- Low blood count
- Weight loss
- Kidney complications
- Chest pain
Symptoms of Lupus in women
Women are more likely to experience the following symptoms [7]:
Signs of Lupus in men
Lupus is commonly thought to affect only women, but males can also be affected. In addition, men with Lupus tend to experience more severe symptoms [8].
Symptoms that occur more commonly in males include:
What Are The Complications Of Lupus?
In addition to the mild to severe symptoms associated with the autoimmune condition, Lupus also affects the following organs [9]:
- Kidneys
- Lungs
- Central nervous system
- Blood vessels
- Blood
- Heart
Lupus
patients
are
more
likely
to
contract
infections
since
both
the
disease
and
its
treatment
weaken
the
immune
system.
Common
infections
include
urinary
tract
infections,
respiratory
infections,
yeast
infections,
salmonella,
herpes
and
shingles.
The
condition
can
also
cause
bone
tissue
death
and
pregnancy
complications.
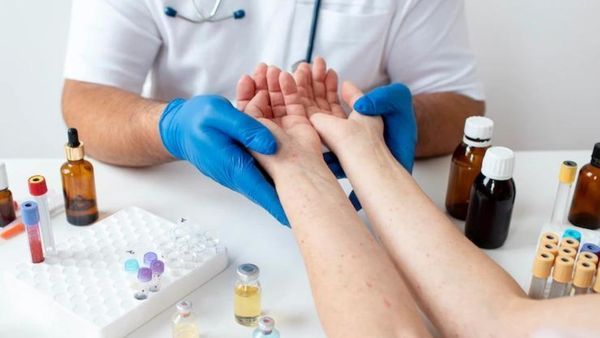
How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
According to the American College of Rheumatology, the diagnosis of lupus can be confirmed if a person meets four of the 11 criteria.
The
11
criteria
are
as
follows:
1.
Malar
rash
2.
Discoid
rash
3.Photosensitivity
4.Oral
or
nose
ulcers
5.Nonerosive
arthritis
6.Pericarditis
or
pleuritis
7.Kidney
disorder
8.Neurologic
disorder
9.Hematologic
(blood)
disorder
10.Immunologic
disorder
11.Positive
ANA
results
How Is Lupus Treated?
The
treatment
or
management
of
lupus
may
be
assisted
by
a
variety
of
treatments
and
home
remedies
[10].
It
is
important
to
discuss
with
your
doctor
whether
you
should
be
treated
and
what
medications
to
use
in
order
to
determine
whether
you
should
be
treated.
- Does lupus get worse with age?
Symptoms of lupus decline with age, but those you already have may worsen. The accumulation of damage over time may result in the need for joint replacements or other forms of treatment.
- How long does a person with lupus live?
Lupus patients can expect a normal life expectancy if they receive close follow-up and treatment.
- What does lupus do to a person?
If you have lupus, you may experience joint pain, skin sensitivities and rashes, and problems with your internal organs (brain, lungs, kidneys, and heart). In addition, you may experience various symptoms in waves, known as flare-ups. Sometimes, lupus symptoms may be mild or non-existent (meaning they have been in remission for some time).
- How does a person get lupus?
Some people most likely to develop lupus due to their genes may experience symptoms caused by sunlight, stress, smoking, certain medications, or viruses. The most common cause of lupus is oestrogen, which is higher during pregnancy. Problems with the immune system are also common.
-
 disorders cureSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatments And Prevention
disorders cureSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatments And Prevention -
 wellnessWorld Autoimmune Arthritis Day (May 20): Autoimmune Diseases And Types
wellnessWorld Autoimmune Arthritis Day (May 20): Autoimmune Diseases And Types -
 nutrition11 Impressive Health Benefits Of Fish Oil
nutrition11 Impressive Health Benefits Of Fish Oil -
 newsResearch Suggests Exercise Helps Those Suffering From Lupus; Foods To Should Eat When You Have Lupus
newsResearch Suggests Exercise Helps Those Suffering From Lupus; Foods To Should Eat When You Have Lupus -
 wellness9 Out Of 10 Patients With Lupus Are Women! Read To Know Its Early Warning Signs
wellness9 Out Of 10 Patients With Lupus Are Women! Read To Know Its Early Warning Signs -
 wellnessAutoimmune Diseases That Every Woman Should Know About
wellnessAutoimmune Diseases That Every Woman Should Know About -
 wellness7 Early Signs Of Lupus You Should Know About
wellness7 Early Signs Of Lupus You Should Know About -
 pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread?
pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread? -
 healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS? -
 healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy
health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



