Latest Updates
-
 Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell
Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell -
 Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress
Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress -
 Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner
Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner -
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause -
 Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft
Ralph Lauren Showcases ‘Jhumkas’ At Paris Fashion Week, Rekindling Debate On Credit For Indian Craft -
 Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem
Viral Video: Pakistani Family Celebrates India’s T20 World Cup Victory With Cake, Sings Indian National Anthem -
 Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend
Who Is Aditi Hundia? Viral Video Shows Ishan Kishan Celebrating India’s T20 World Cup Win With Girlfriend -
 India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message
India Seal Historic T20 World Cup Win: Samson Tournament Star, Bumrah Match Hero, Dhoni Posts Special Message -
 Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress
Horoscope for Today March 09, 2026 - Small Steps, Big Progress -
 International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
International Women’s Day 2026: 7 Powerful Ayurvedic Foods Every Woman Should Start Adding To Her Daily Diet
The Complete Guide to Melanoma: Symptoms, Causes, and Cure
Everything you need to know about malignant melanoma.
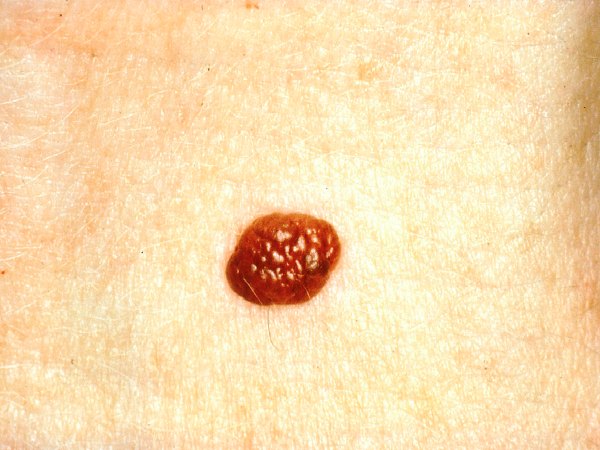
Melanoma, a.k.a malignant melanoma, is the most dangerous skin cancer of them all.
It is caused by the abnormal transformation of melanocytes, which are cells that produce the tanning pigment melanin in our body.
And while reports suggest that nearly 3.1 million people are affected by it every year, the number is believed to increase even more now as global warming and pollution continue to damage the Earth's atmosphere, which is responsible for blocking out the harmful UV rays of the sun.
In fact, Australia and New Zealand have the highest rate of melanoma in the world, which can be attributed to the damaged ozone layer above these regions.
Given all these alarming facts, it's very important for you to know the exact causes and symptoms of melanoma.
Especially if you have multiple moles on your body since birth.

What are the Causes of Melanoma?
While nothing causes cancer 100% of the time, the following are some of the biggest risk factors for developing melanoma.

#1 Exposure to UV Rays of the Sun
There are 2 types of UV rays in sunlight: UVA and UVB. And UVB is the more dangerous of the two as it breaks down the DNA of skin cells once it is absorbed through the skin.
In fact, caucasians (whites) are at a greater risk of getting melanoma because they lack the pigment melanin in their skin, which is responsible for protecting you from UV rays.
No wonder the indigenous population of tropical countries and continents, like India and Africa, are dark-skinned.
They biologically produce more melanin to protect themselves from the abundant sunlight these regions receive throughout the year.

#2 Using Indoor Tanning Booths
Tanning booths bombard your skin with artificial UV rays to increase melanin production in your skin.
Unfortunately, chronic exposure to these UV rays before the age of 30 has been documented to increase the risk of getting melanoma by almost 75%!

#3 Family History of Melanoma
Certain genes have been recognized that increase the risk of melanoma. Like the recessive gene MC1R that produces red hair.
Maybe that's why melanoma is also quite prevalent in Northern Europe and America.

#4 Presence of Moles on Your Skin
25% of all melanoma cases originate from benign moles on the skin.
And this risk is even greater in those who have multiple atypical, dysplastic, or giant melanocytic nevi (mole).

#5 Genetic Defect: Xeroderma Pigmentosum
Xeroderma Pigmentosum is a rare genetic disease where the individual is born with extreme sensitivity to UV rays because the body is naturally incapable of repairing the damage caused by it.
That's why those who are born with this defect are at a very high risk of developing malignant melanoma.
Melanoma Symptoms and Signs of Metastasis
It is estimated that even after early detection, 20% of all melanoma cases still become malignant.
That's why it is very important to know the symptoms of melanoma so that your doctor can intervene early and prevent it from metastasizing.

And it's not very difficult to remember.

In fact, the nodular form of this cancer (which is also the most dangerous form of melanoma), also has its very own mnemonic.
E - Elevated above the skin's surface.
F - Firm to touch.
G - Grows over time.
Stages of Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer for a reason.
It is because on the outside it looks small and innocuous, but deep inside it keeps growing and growing until one day it breaks into your blood vessels and then metastasizes all over your body.
The following are the various stages it goes through before it culminates into metastasis.

Stage 0
Also called cancer in-situ (or precancerous lesion).
In this stage, abnormal melanocytes are only present in the outermost epidermis of the skin.

Stage I
This stage is further divided into 2 parts.
IA - The cancerous growth has affected less than 1mm of your skin's thickness from the surface, and there is no ulceration.
IB - The small lesion has now ulcerated, or it is 1 - 2mm thick without ulceration.

Stage II
This stage also has further subdivisions.
IIA - The 1 - 2mm thick cancer has now ulcerated, or it has grown to 2 - 4mm thickness without ulceration.
IIB - The 2 - 4mm thick cancer has ulcerated, or it has grown larger than 4mm without ulceration.
IIC - The large lesion (greater than 4mm) has now ulcerated.

Stage III
The size of the cancer doesn't matter anymore since cancer cells have now spread to one to more lymph nodes in the body, or has created satellite tumors that are within 2cm from the original tumor.

Stage IV
Melanoma that has reached this stage is called malignant melanoma because now the cancer cells have spread all over the body.
The most common sites of metastasis are lungs, liver, and brain.
How to Protect Yourself From Melanoma
The only way you can prevent a diagnosis is by protecting yourself from the risk factors of melanoma.
And while hereditary risks put you at a greater danger than most others, you can still use the following tips to reduce the likelihood of skin cancer.

5 Ways to Treat Melanoma
Getting a cancer diagnosis is the worst nightmare of everyone's life.
So if you have melanoma, the following are the various ways through which your doctor can help you fight it.

#1 Surgery
Surgery is an option only when the melanoma is in its early stages.
In this technique, the entire tumor and 1 - 2cm of healthy tissue is excised to prevent malignant growth and recurrence.
The procedure is usually followed by skin grafting to patch up the unsightly hole.

#2 Chemotherapy
Killer drugs that are directly delivered to your body through the blood, muscle, or CSF (spinal fluid) fall in this category.
This therapy is usually used as an adjunct along with surgery for the early stages of melanoma.

#3 Radiation Therapy
Melanoma can also be treated by irradiating the area with external radiation.
#4 Immunotherapy
This form of treatment is designed to boost your immunity to help fight the cancer cells.

#5 Targeted Therapy
These are drugs that are designed to specifically target certain proteins and compounds in the cancer cells that normal cells lack. This way the cancer cells are killed off while the healthy tissues remain intact.
One such targeted therapy is oncolytic virotherapy that has shown promising results during the treatment of melanoma.
Was This Article Helpful?
Yes?
Then please share it on social media so others can read it too.
Stages of Melanoma image source - NIH USA



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












