Latest Updates
-
 All Eyes On Kritika Kamra As She Wears Stunning White Bridal Gown At Reception With Gaurav Kapur
All Eyes On Kritika Kamra As She Wears Stunning White Bridal Gown At Reception With Gaurav Kapur -
 The MS Dhoni Effect: How Athletes Are Influencing the Indian Men's Everyday Jewellery Style
The MS Dhoni Effect: How Athletes Are Influencing the Indian Men's Everyday Jewellery Style -
 World Sleep Day 2026: The Science Behind Why Women Need More Sleep
World Sleep Day 2026: The Science Behind Why Women Need More Sleep -
 World Sleep Day 2026: Date, Theme, History, and the Importance of Healthy Sleep
World Sleep Day 2026: Date, Theme, History, and the Importance of Healthy Sleep -
 Papamochani Ekadashi 2026: Is the Fast on March 14 or 15? Know the Correct Date
Papamochani Ekadashi 2026: Is the Fast on March 14 or 15? Know the Correct Date -
 LPG Shortage? Try These Healthy Meals That Don’t Need Cooking
LPG Shortage? Try These Healthy Meals That Don’t Need Cooking -
 This Week’s OTT Releases (March 9–15): What To Watch On Netflix, JioHotstar, ZEE5, Prime Video, And SonyLIV
This Week’s OTT Releases (March 9–15): What To Watch On Netflix, JioHotstar, ZEE5, Prime Video, And SonyLIV -
 Horoscope for Today Mar 13, 2026 - Small Choices, Steady Progress
Horoscope for Today Mar 13, 2026 - Small Choices, Steady Progress -
 Alvida Jumma 2026 Date: 13th or 20th March? Everything You Should Know About The Last Friday Of Ramadan
Alvida Jumma 2026 Date: 13th or 20th March? Everything You Should Know About The Last Friday Of Ramadan -
 Rashmika Mandanna Breaks Silence On Mother’s Viral Audio Leak, Warns Of Legal Action In 24 Hours
Rashmika Mandanna Breaks Silence On Mother’s Viral Audio Leak, Warns Of Legal Action In 24 Hours
Kidney Stones: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment And Prevention
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis or nephrolithiasis) are one of the most common illnesses in India. The main function of the kidney is to flush out all the excess water and blood impurities in the form of urine [1] . Certain substances like calcium oxalate, amino acids, and uric acid are left behind in the form of tiny particles and when the concentration of those accumulated substances increases, they get converted into hard and sharp crystalline stones known as kidney stones.
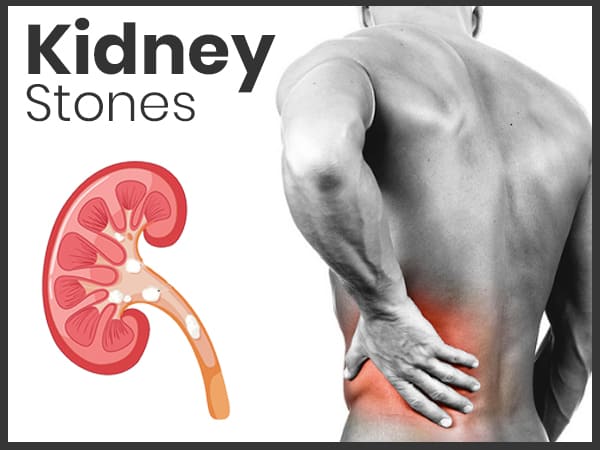
Kidney stones up to the size 3 mm, can pass through urine but bigger kidney stones can create extreme pain and blood discharge in the urine. The pain is caused when the stones get stuck in the ureter, a tube that connects the kidney and the bladder, and block the passage of the urine [2] . Kidney stones can also grow to the size of a golf ball.
Types Of Kidney Stones
- Calcium stones: Such stones are usually caused due to the buildup of calcium oxalate, a naturally occurring compound in foods like spinach, almonds, grits and cocoa powder.
- Cystine stones: Cystine stones are as a result of a hereditary disorder (cystinuria) in which the kidney excretes an excessive amount of amino acid in the urine [3] .
- Uric acid stones: Such type of stones are formed in people who usually don't drink enough water or loses too much water, consume high protein diet and suffers from gout.
- Struvite stones: Such type of stones occur as a result of an infection like urinary tract infection. In this condition, the stones grow quickly and unnoticeably.

Symptoms Of Kidney Stones
The symptoms of kidney stones depend on their size. If the kidney stones are smaller in size, they won't create much trouble and will pass easily through the urine. The large-sized kidney stones move towards the ureter and block the path between the kidney and the bladder. Under this condition, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- Cloudy/red urine: Urine may become reddish and get a cloudy appearance accompanied by a foul smell. The reddish discolouration of the urine is usually due to injury to either ureter or urethra or even due to kidney injury. The colour varies according to the site.The presence of these bacteria also causes a burning sensation while passing urine. Irritation in the kidney tissues may sometimes lead to red-coloured urine [4] .
- Loin to groin pain: Pain is one of the basic symptoms of kidney stones. The pain is experienced in the lower abdomen. The pain occurs when ureter tries to push down the stone in the urinary bladder [5] . It is a cramping pain in the lower abdomen, there are also chances of inflammation.
- Frequent urination: One of the side effects can be a urine infection. The blockage of the urine passage leads to the feeling of incomplete urination. Frequent urination along with pain or burning sensation should not be ignored.
- Flu-like symptoms: In the advanced stages of the disease, the patient might experience fatigue, fever and body ache. Vaginal pain may also be experienced. It can be treated with home remedies [5] .
Causes Of Kidney Stones
Several factors lead to the formation of kidney stones in our body. Some of the common causes are as follows:
- Inadequate amount of fluid intake is one of the basic causes of kidney stones. Less water consumption means less flushing out of waste and growing concentration of other substances, which gradually form the stone [6] .
- Kidney stones can also be hereditary [7] .
- Chemical concentration in urine i.e., concentration of calcium, uric acid etc. also leads to the formation of the stone.
- Obesity is another reason for kidney stones formation as it changes the urine acid levels and leads to stones formation.
- Urinary tract infections may sometimes be the cause [8]
- Medical conditions like Crohn's disease, medullary sponge kidney, hyperparathyroidism, and Dent's disease
- People suffering from inflammatory bowel disease are more likely to suffer.
- Drugs containing diuretics, calcium, and protease inhibitor: indinavir
- Surgeries like gastric bypass surgery
Complications Of Kidney Stones
The most deadly complications on the lookout for kidney stones are hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, abscess formation and kidney failure.
Diagnosis Of Kidney Stones
To diagnose for the kidney stones in your body, there are several tests and procedures which need to be followed [9] . The most important factor in diagnosing kidney stone is a physical examination by a doctor and image-based studies.
The tests are as follows:
- Urine test
- Blood test
- CT scan or X-ray
- Ultrasound
- Intravenous urography
- Analysis of the passed stones from the kidney
Treatment For Kidney Stones
Depending upon the type and size of kidney stones, treatment is carried out.
The non-invasive treatment of kidney stones include the following:
- Drinking water up to 2 to 2.8 litres a day [6] .
- Pain relievers like ibuprofen and naproxen sodium to relieve pain caused due to the stones.
- Medications like alpha-blocker to relax the ureter muscles for the stones to pass off easily to the bladder [10] .
For the large kidney stones, extensive treatment is required which includes the following:
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) to break kidney stones by strong vibrations [11]
- Surgery for big kidney stones
- Ureteroscope to break down stones so that it could easily pass through the urine [12] .
- Parathyroid gland surgery
10 Home Remedies For Kidney Stones
How To Prevent Kidney Stones
There are certain lifestyle changes with which a person can prevent the formation of kidney stones. The changes are as follows:
- Don't miss out on the water as less water intake is the primary cause of kidney stones.
- Opt for minimal salted foods and veggie proteins like legumes.
- Reduce the intake of oxalate-rich foods like soy products, nuts, etc.
- Connect to your doctor before starting calcium supplements.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
- [1] Blantz, R. C., Deng, A., Miracle, C. M., & Thomson, S. C. (2007). Regulation of kidney function and metabolism: a question of supply and demand. Transactions of the American Clinical and Climatological Association, 118, 23–43.
- [2] Alelign, T., & Petros, B. (2018). Kidney Stone Disease: An Update on Current Concepts. Advances in urology, 2018, 3068365. doi:10.1155/2018/3068365
- [3] Han, H., Segal, A. M., Seifter, J. L., & Dwyer, J. T. (2015). Nutritional Management of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis). Clinical nutrition research, 4(3), 137–152. doi:10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.137
- [4] Khan, S. R., Pearle, M. S., Robertson, W. G., Gambaro, G., Canales, B. K., Doizi, S., … Tiselius, H. G. (2016). Kidney stones. Nature reviews. Disease primers, 2, 16008. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.8
- [5] Favus, M. J., & Feingold, K. R. (2018). Kidney Stone Emergencies. In Endotext [Internet]. MDText. com, Inc..
- [6] Xu, C., Zhang, C., Wang, X. L., Liu, T. Z., Zeng, X. T., Li, S., & Duan, X. W. (2015). Self-Fluid Management in Prevention of Kidney Stones: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine, 94(27), e1042. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001042
- [7] Halbritter, J., Seidel, A., Müller, L., Schönauer, R., & Hoppe, B. (2018). Update on Hereditary Kidney Stone Disease and Introduction of a New Clinical Patient Registry in Germany. Frontiers in pediatrics, 6, 47. doi:10.3389/fped.2018.00047
- [8] Schwaderer, A. L., & Wolfe, A. J. (2017). The association between bacteria and urinary stones. Annals of translational medicine, 5(2), 32. doi:10.21037/atm.2016.11.73
- [9] Sakhaee, K., Maalouf, N. M., & Sinnott, B. (2012). Clinical review. Kidney stones 2012: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 97(6), 1847–1860. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3492
- [10] Lipkin, M., & Shah, O. (2006). The use of alpha-blockers for the treatment of nephrolithiasis. Reviews in urology, 8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4), S35–S42.
- [11] Junuzovic, D., Prstojevic, J. K., Hasanbegovic, M., & Lepara, Z. (2014). Evaluation of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): Efficacy in Treatment of Urinary System Stones. Acta informatica medica : AIM : journal of the Society for Medical Informatics of Bosnia & Herzegovina : casopis Drustva za medicinsku informatiku BiH, 22(5), 309–314. doi:10.5455/aim.2014.22.309-314
- [12] Oliver, R., Ghosh, A., Geraghty, R., Moore, S., & Somani, B. K. (2017). Successful ureteroscopy for kidney stone disease leads to resolution of urinary tract infections: Prospective outcomes with a 12-month follow-up. Central European journal of urology, 70(4), 418–423. doi:10.5173/ceju.2017.1549




 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












