Latest Updates
-
 Vijay Deverakonda, Rashmika Mandanna’s Pradhanam-Mehendi Looks Redefine Celebrity Wedding Fashion This Year
Vijay Deverakonda, Rashmika Mandanna’s Pradhanam-Mehendi Looks Redefine Celebrity Wedding Fashion This Year -
 Lucky Colours For March 2026 According To Zodiac Signs And The Shades You Should Wear
Lucky Colours For March 2026 According To Zodiac Signs And The Shades You Should Wear -
 Randeep Hooda Becomes Father On His Dad’s Birthday, Shares First Baby Photos In Heartwarming Instagram Post
Randeep Hooda Becomes Father On His Dad’s Birthday, Shares First Baby Photos In Heartwarming Instagram Post -
 World Kidney Day 2026: History, Significance And Theme Behind This Global Health Awareness Day
World Kidney Day 2026: History, Significance And Theme Behind This Global Health Awareness Day -
 Who Is Charulatha Remesh? Sanju Samson’s ‘Dear Pondatti’ Post After India’s T20 World Cup Victory Wins Hearts
Who Is Charulatha Remesh? Sanju Samson’s ‘Dear Pondatti’ Post After India’s T20 World Cup Victory Wins Hearts -
 Sheetala Saptami 2026: Significance, Vrat Katha And Why Families Eat Cold Food And Avoid Cooking This Day
Sheetala Saptami 2026: Significance, Vrat Katha And Why Families Eat Cold Food And Avoid Cooking This Day -
 Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell
Suryakumar Yadav Takes T20 World Cup Trophy To 526 Year Old Adalaj Stepwell -
 Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress
Horoscope for Today March 10, 2026 - Calm Energy, Steady Progress -
 Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner
Women Car Rally Held In Gurugram On International Women’s Day, Boldsky Collaborates As Media Partner -
 The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
The Protein Gap In Women’s Diets: Gynaecologist Explains Why This Nutrient Matters From Puberty To Menopause
International Day Against Nuclear Tests 2019: A Look At The Worst Nuclear Disasters In History
The International Day against Nuclear Tests is observed on 29 August every year. Established on 2 December 2009 at the 64th session of the United Nations General Assembly, the day was entrenched with idea of increasing the awareness of nuclear weapon tests and nuclear explosions and the need to end the nuclear tests, to attain the goal of a nuclear-weapon-free world [1] .
The resolution was proposed by Kazakhstan and by May 2010, all the state parties that signed the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons took a vow to achieve 'peace and security of a world without nuclear weapons'.
Every year, the day is observed by conducting symposia, conferences, exhibits, competitions, publications, lectures, media broadcasts and various other events, to ardently spread awareness [2] .
What Is Nuclear Weapon Testing?
Termed as experiments, nuclear weapon tests are carried out to determine the effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability of nuclear weapons. The tests aid the understanding of how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions [3] .
Although conducted for the aforementioned purposes, nuclear tests are mostly used as an index to show off the country's military strength as well as scientific proficiency' with most tests being carried out for political conation.
The first-ever nuclear test was carried out by the United States at the Trinity site on 16 July 1945. It was in 1963, UK, US and Soviet Union (3 of the 4 nuclear states), along with various other non-nuclear states signed the Limited Test Ban Treaty which requested to end the nuclear weapon testing in the atmosphere, underwater, or in outer space [4] .
On this International Day Against Nuclear Tests, let's take a look at the worst nuclear disasters recorded in history.
Worst Nuclear Disasters In History
According to UN Secretary-General António Guterres, "the legacy of nuclear testing is nothing but destruction".
After the first-ever nuclear testing of 1945, there have been 2000 or more testing done. Nuclear technology produces radioactive waste during any reactor accidents or waste storage leaks. A nuclear disaster can cause a severe and drastic impact on human beings as well as animals. From increased cancer rates to generational problems, the residues can destroy the balance of the environment [5] .

The number of deaths and illnesses that are caused by a nuclear disaster are difficult to be traced, therefore, it is usually characterised by the rating on the International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale (INES), a form of metrics developed in 1990 as a way to measure the destruction caused by nuclear disasters.
According to INES, the different levels of nuclear disasters are as follows [6] :
- Level 7 - Major Accident
- Level 6 - Serious Accident
- Level 5 - Accident With Wider Consequences
- Level 4 - Accident With Local Consequences
- Level 3 - Serious Incident
- Level 2 - Incident
- Level 1 - Anomaly
- Level 0 - Deviation
Now, take a look at the worst nuclear disasters recorded in history [7] [8] .
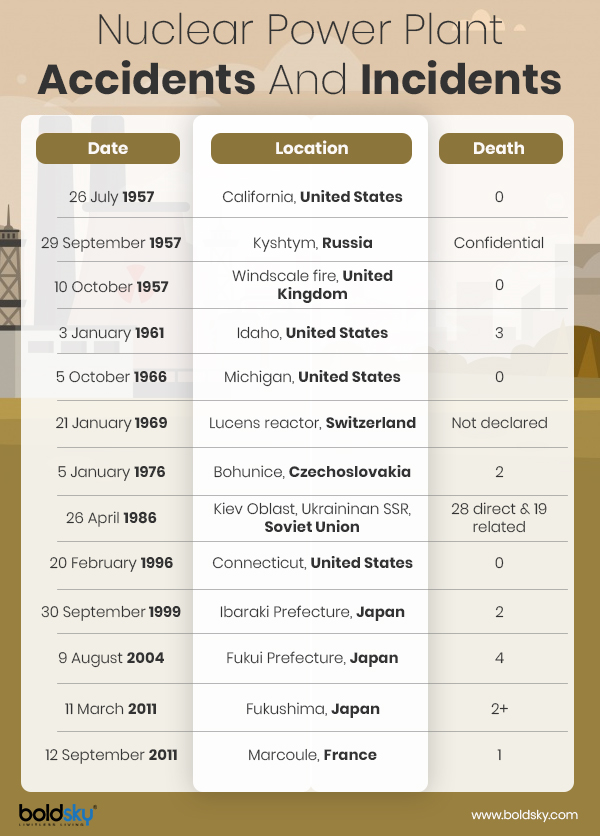
1. Chernobyl, Ukraine 1986 - Level 7
The Chernobyl Nuclear disaster is considered to be the worst nuclear disaster to date. It is one amongst the only two incidents classified at Level 7. On 26 April 1986, the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine exploded during testing, which continued for a period of 9 days, with fires and radiation emissions.
31 immediate deaths and an estimated 4,000 premature deaths were reported. An 18.6-mile radius area near surrounding the factory is still closed and has been named the Chernobyl Disaster Exclusive Zone.
2. Fukushima, Japan 2011 - Level 7
The most recent nuclear disaster was a series of equipment failures, nuclear meltdowns and releases of radioactive materials at the Fukushima, Nuclear Power Plant. The incident took place following the Tohoku Tsunami on 11 March 2011.
The largest since the Chernobyl disaster of 1986 and marked the second severest nuclear disaster, it was the tragic earthquakes that caused the meltdowns at nuclear power plants. It caused the death of two people and an approximate of 2,202 from evacuation (till date).
3. Kyshtym, Russia 1957 - Level 6
The disaster took place on 29 September 1957 at Mayak, a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in the Soviet Union. The radioactive contamination was the third most serious nuclear disaster ever recorded behind the Chernobyl Disaster and Fukushima Daiichi Disaster. 22 villages were exposed to the radiation and caused the death of 200 people and contaminated the nearby rivers and soil.
More than 10,000 people were evacuated from the city and it took more than 2 years to completely evacuate the sites.
4. Windscale Fire (Sellafield), UK 1957 - Level 5
The Windscale Fire is the worst nuclear disaster recorded in Great Britain's history. The disaster took place on the 10 October 1957. The accident occurred when one of the two nuclear piles caught fire and thus, released substantial amounts of radioactive contamination.
The disaster caused 240 cancer cases, although there is still an uncertainty in the connection between the Windscale Fire and cancer rates.
5. Three Mile Island Accident, Pennsylvania USA 1979 - Level 5
One of the most critical nuclear disaster recorded in American history, the Three Mile Island accident occurred on 28 March 1979. The incident occurred in an event of large amounts of nuclear reactor coolant being leaked out from reactor number 2 at the Nuclear Generating Station near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, United States.
The late detection of the leak delayed the damage control and has indeed caused a panic in the society in regards to nuclear weaponry.
6. Goiania Accident, Brazil 1987 - Level 5
Goais, a state in Brazil was made the victim to nuclear disaster on 13 September 1987. The contamination was reported when an old radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site and caused the death of 4 people, and 249 people had significant amounts of radioactive material in or on their body.
7. SL-1 Experimental Power Station, Idaho USA 1961 - Level 4
A USA army experimental nuclear power reactor underwent faced a steam explosion and meltdown on 3 January 1961, killing the 3 operators working there. The disaster was caused due to the improper removal of the control rod which is responsible for absorbing neutrons in the reactor core.
8. Saint Laurent, France 1969 - Level 4
The most serious of Nuclear disaster in French history, the incident occurred on 17 October 1956 when 50 kg of uranium in one of the gas-cooled reactors began melting.
9. Buenos Aires, Argentina 1983 - Level 4
On 23 September1983, a minor mistake in the fuel plate reconfiguration by the operator working in the plant caused his demise. The mistake caused the operator to absorb 2000 rad of gamma and 1700 rad of neutron radiation, which spread outside of the reactor room, resulting in 17 people absorbing it too.
10. Tokaimura, Japan 1999 - Level 4
The disaster took place when a group of unqualified workers mixed large amounts of highly enriched uranium in a precipitation tank. Two of the workers died eventually with other 56 plant workers and 21 civilians being exposed to the radiation.
- [1] Ohtsuru, A., Tanigawa, K., Kumagai, A., Niwa, O., Takamura, N., Midorikawa, S., ... & Clarke, M. (2015). Nuclear disasters and health: lessons learned, challenges, and proposals. The Lancet, 386(9992), 489-497.
- [2] Bromet, E. J. (2014). Emotional consequences of nuclear power plant disasters. Health physics, 106(2), 206.
- [3] Thompson, J. (1985). Psychological aspects of nuclear war.
- [4] Behere, P. B., Chougule, K. N., & Syyed, S. (2017). Psychological impact of nuclear disasters. In Proceedings of the innovative technology for rural development and their commercialisation: souvenir.
- [5] Wheatley, S., Sovacool, B. K., & Sornette, D. (2016). Reassessing the safety of nuclear power. Energy Research & Social Science, 15, 96-100.
- [6] Labib, A., & Harris, M. J. (2015). Learning how to learn from failures: The Fukushima nuclear disaster. Engineering Failure Analysis, 47, 117-128.
- [7] Imanaka, T. (2018). The nuclear disaster in Ural, the fire accident at the Windscale reactor and the submarine criticality accident near Vladivostok (No. KURRI-EKR—23).
- [8] Wu, S. S. (2016). Nuclear disaster in Taiwan: a multidimensional security challenge. Global Change, Peace & Security, 28(3), 289-305.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












