Latest Updates
-
 How Obesity Impacts Fertility, Menstrual Health, And Pregnancy Outcomes
How Obesity Impacts Fertility, Menstrual Health, And Pregnancy Outcomes -
 Arjun Tendulkar Marries Saaniya Chandhok In Grand Mumbai Wedding; First Pics Go Viral
Arjun Tendulkar Marries Saaniya Chandhok In Grand Mumbai Wedding; First Pics Go Viral -
 UK07 Rider Anurag Dobhal Shares Emotional Video, Alleges Harassment After Inter-Caste Marriage
UK07 Rider Anurag Dobhal Shares Emotional Video, Alleges Harassment After Inter-Caste Marriage -
 How a Blockbuster Ignited a Popcorn Boom: The Dhurandhar Effect and the Rise of Gourmet Cinema Snacks in India
How a Blockbuster Ignited a Popcorn Boom: The Dhurandhar Effect and the Rise of Gourmet Cinema Snacks in India -
 Splitsvilla X6 Episode 25 OTT Release: Tejasswi Prakash’s Cameo, Karan Calls Her His Real-Life Ideal Match
Splitsvilla X6 Episode 25 OTT Release: Tejasswi Prakash’s Cameo, Karan Calls Her His Real-Life Ideal Match -
 Rashmika and Vijay Deverakonda’s Hyderabad Reception: Decoding the Looks, Moments, And Who Came
Rashmika and Vijay Deverakonda’s Hyderabad Reception: Decoding the Looks, Moments, And Who Came -
 Horoscope for Today March 05, 2026 - Small Habits, Big Daily Wins
Horoscope for Today March 05, 2026 - Small Habits, Big Daily Wins -
 Holi 2026: The Aftercare Routine Your Skin And Hair Will Thank You For
Holi 2026: The Aftercare Routine Your Skin And Hair Will Thank You For -
 Over-Scrubbing After Holi? You Could Be Damaging Your Skin Microbiome, Not Just Removing Colour
Over-Scrubbing After Holi? You Could Be Damaging Your Skin Microbiome, Not Just Removing Colour -
 Horoscope for Today March 04, 2026 - Practical Steps for Calm Wins
Horoscope for Today March 04, 2026 - Practical Steps for Calm Wins
How Does Prone Positioning Help In The Management Of COVID-19 In Patients?
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 spread, the researchers have informed people to cover their mouth, nose and eyes as the coronavirus primarily infects the lungs by entering through these mucous membranes.

The virus worsens the lung condition and may cause serious lung problems such as pneumonia, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis. The primary symptom of all these is shortness of breath due to lung damage.
Multiple treatment methods were introduced to improve severe lung conditions induced due to COVID-19.
Among those methods, the prone position has been widely used as well as recommended by medical health experts globally as adjuvant therapy for improving oxygenation in COVID-19 patients.
Let's understand in details the prone positioning and its effectiveness in the management of COVID-19.
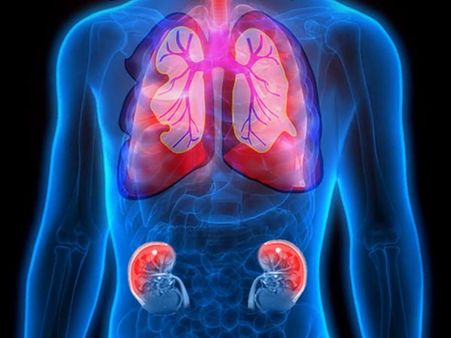
COVID-19 And ARDS
COVID-19 is directly related to ARDS as its severe stage probably leads to lung conditions like ARDS and pneumonia. ARDS is characterised by respiratory failure, ventilation and perfusion mismatch and accumulation of fluid in the air sacs. A report says that mortality rate linked to ARDS is between 22-44 per cent. [1]
ARDS is caused by many factors but after the outbreak of COVID-19, it was noted that COVID-19 symptoms rapidly get progressive in people with ARDS. The characteristics of COVID-19-related ARDS patients and ARDS due to other factors are found to be different when evaluated.
COVID-19-related ARDS mainly affects the respiratory system with minor injuries to other organs while ARDS due to other factors can cause heart failure or renal damage along with impairment of the lungs.
The onset of symptoms in the prior is between 8-14 days while the latter shows symptoms within a week. [2] Also, in COVID-19 induced ARDS, the common symptom is dry cough while in normal ARDS condition, a foamy or bubble-like mucus is formed.
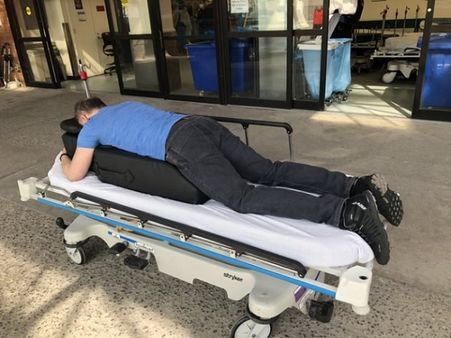
What Is Prone Positioning?
Prone positioning refers to a body position that promotes improved gas exchange in the lungs in people with ARDS. The method has shown a significant decrease in mortality and improved lung function.
Usually, in the treatment of ARDS, ventilators are required for days to improve oxygenation which results in increased hospital cost. This is why prone positioning is recommended as it comes with no cost, helps reduce pleural pressure and improve the oxygenation in the lungs. It is mainly used as a rescue strategy in many severe cases.
Prone positioning is done by bending on your knees (in a dog-like position), joining both the hands on the ground (like you do while sleeping on a table) and keeping your head above your hands. Then, deep breaths are taken in and coughed out.
There are other prone positions like lying flat on your stomach with pillows under your chest. However, the above method is considered effective. [3]
The prone position helps mobilise the thick mucus present in the bottom portion of the lungs so that an individual can cough it out. This position also improves oxygenation in the lung region which is close to the heart as sometimes, due to fluid overload in the lungs, the heart gets damaged leading to heart failure.
Many studies demonstrate that prone positioning causes homogeneous aeration of the lungs. The CT scan and aeration and ventilation results also show improved homogeneity in this position. This improves the blood flow in the dorsal and injured lung regions and helps in improving the condition.
Image source: www.geekwire.com/
Does Prone Positioning Help In Managing COVID-19 Patients?
Prone positioning is highly effective when carried out by patients with severe ARDS and applied for at least 12 hours a day. Patients with mild symptoms are usually not recommended. Also, some studies show side effects of this position such as accidental removal of the tracheal tube, facial oedema, bending of the chest tube, excess salivation and stomach reflux.[4]
A study talks about a 50-year-old man with COVID-19-related ARDS. He was successfully treated with prone positioning with improved ventilation and drainage of secretions from the lungs. In the same study, the position was again applied to 10 more patients with an average age of 41 years and with 30 per cent of them with preexisting conditions such as diabetes. The results were amazing as they all were discharged within an average of 4.8 days, with no problems later. [5]
Therefore, it is concluded that prone positioning can help reduce mortality and manage COVID-19 patients.

To Conclude
Prone positioning has been for a long time as a therapy to improve oxygen levels in the lungs. Over time, several studies have shown its efficacy for survival in conditions such as ARDS, pneumonia and even in recent COVID-19.
Though the effectiveness of this position can be seen only in selected patients, it can be used as an important strategy to reduce the mortality risk in people with COVID-19-related ARDS.



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications












