Just In
- 4 hrs ago

- 5 hrs ago

- 8 hrs ago

- 15 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Finance
 FREE, FREE, FREE! 3:1 Bonus: Pharma Stock Hits Back-To-Back Upper Circuits; 500 Shares To Earn Rs 1,69,500
FREE, FREE, FREE! 3:1 Bonus: Pharma Stock Hits Back-To-Back Upper Circuits; 500 Shares To Earn Rs 1,69,500 - Sports
 Manchester City vs Chelsea LIVE Streaming: Where to Watch FA Cup Semi-Final in India, UK, USA and Other Countries
Manchester City vs Chelsea LIVE Streaming: Where to Watch FA Cup Semi-Final in India, UK, USA and Other Countries - Movies
 Pukaar Dil Se Dil Tak Promo: Sayli Salunkhe Impresses In First Video Of Sony TV Show, Details About Her Role
Pukaar Dil Se Dil Tak Promo: Sayli Salunkhe Impresses In First Video Of Sony TV Show, Details About Her Role - News
 Chinese President Xi Jinping Orders Biggest Military Reorganisation Since 2015
Chinese President Xi Jinping Orders Biggest Military Reorganisation Since 2015 - Education
 Exam Pressure Does Not Exist; Studying Punctually is Crucial; Says Aditi, the PSEB 2024 Topper
Exam Pressure Does Not Exist; Studying Punctually is Crucial; Says Aditi, the PSEB 2024 Topper - Automobiles
 Suzuki Swift Hatchback Scores 4 Star Safety Rating At JNCAP – ADAS, New Engine & More
Suzuki Swift Hatchback Scores 4 Star Safety Rating At JNCAP – ADAS, New Engine & More - Technology
 Dell Introduces AI-Powered Laptops and Mobile Workstations for Enterprises in India
Dell Introduces AI-Powered Laptops and Mobile Workstations for Enterprises in India - Travel
 Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions
Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions
10 Amazing Nutritional Health Benefits Of Artichokes
Artichoke, also known as Cynara cardunculus, is widely used as a medicinal and dietary plant. It has been used since ancient times in Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The leaves, also known as bracts, are the only edible part in this plant; bracts are connected to a receptacle called head or capitulum, which is rich in bioactive compounds. It is widely cultivated in America, Mediterranean countries and other mildly humid areas with required rich soil.
Artichokes have the appearance of large, toothed leaves with a flower budding in the middle. They can grow up to one metre long and are usually grown through vegetative propagation. They die each year once the flowers fully bloom.

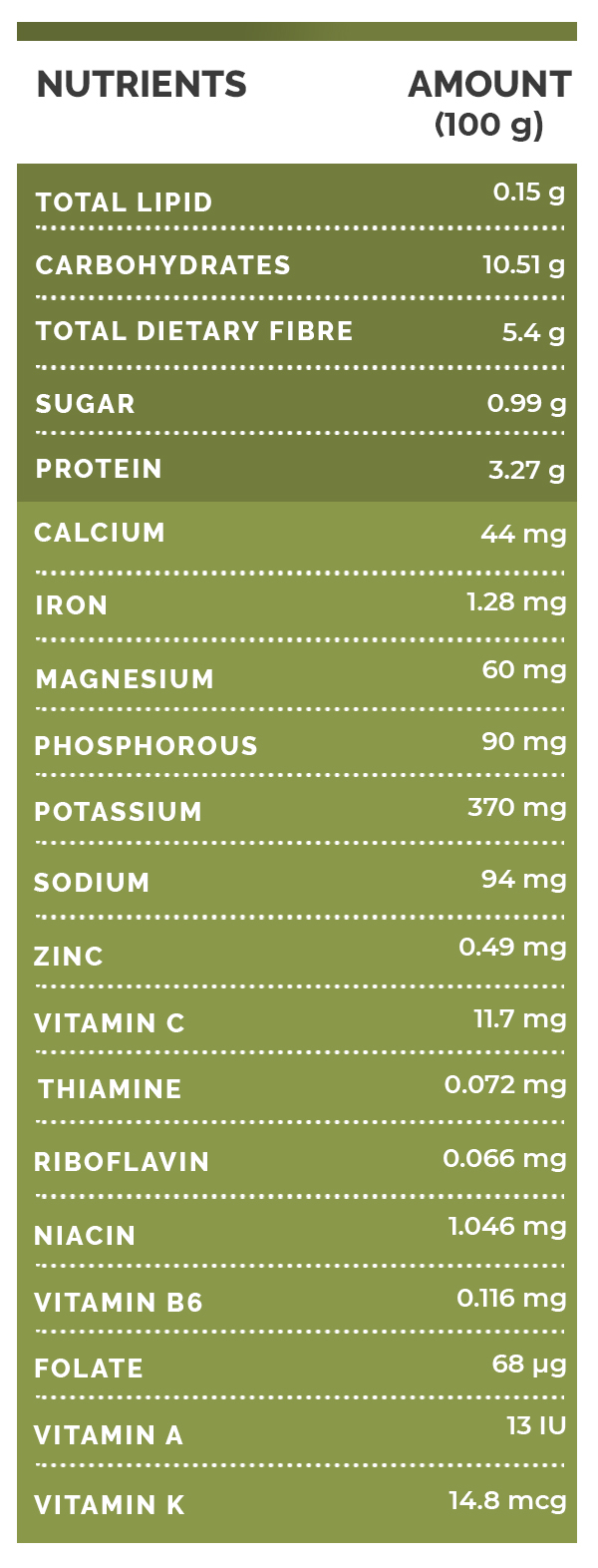
Nutritional Value Of Artichokes [1]
100
grams
of
artichokes
contain
84.94
g
water
and
47
kcal
of
energy.
They
also
contain
3.27
g
of
protein
0.15
g
of
total
lipid
(fat)
10.51
g
of
carbohydrate
5.4
g
of
dietary
fibre
0.99
g
of
sugars
44
mg
of
Calcium
1.28
mg
of
Iron
60
mg
of
magnesium
90
mg
of
phosphorus
370
mg
of
potassium
94
mg
of
sodium
0.49
mg
of
zinc
11.7
mg
of
vitamin
C
0.072
mg
of
thiamine
1.046
mg
of
niacin
0.066
mg
of
riboflavin
0.116
mg
of
vitamin
B6
68
mcg
of
folate
13
IU
of
vitamin
A
14.8
IU
of
vitamin
K
Health Benefits Of Artichokes
1. Rich source of antioxidants and prevents cancer
Artichokes are a potent source of antioxidants [2] . They contain phytonutrients such as gallic acid, rutin, quercetin and cynarin. These antioxidants play an important role in the maintenance and development of cells and immunity. They have the capacity to fight back the pathogenic microbes, and acts as a strong body defence mechanism against multiple diseases [3] .
Antioxidants can also eliminate intracellular tumours or pathogens, thus playing an important role in preventing cancer. Polyphenolic extracts from artichokes possess anticancer and chemopreventive activities [4] . High doses of AE extracts (edible parts of artichokes) can promote apoptosis and decrease the invasive cancer cells in the breast cell line. They reduce cell viability and prevent rapid cell growth. They display excellent inhibitory properties against the invasion of tumour cells.
According to researchers, an experiment proved that 10% fish oil and 1% of artichoke leaves are effective in protection against hepatocellular carcinoma, to some extent. They can also intercept angiogenesis [5] .
2. Helps with liver detoxification and improves digestive health
Artichokes are widely used in the treatment of dyspepsia. The active compounds present inside artichokes influence the plasma lipid levels; the antioxidants such as silymarin when combined, act as a protective shield for liver [6] .
According to research conducted, consumption of artichoke reduces the chances of having E. coli or salmonella in intestines and improves microbial contents inside the gut, thus promoting defence and regeneration [7] . A specific compound named cynarin in artichokes promotes choleretic activity; it facilitates effective production of bile and maintains great gut health. The bile acid concentration increases over time [8] which helps in easier absorption of nutrients and essential fatty acids.
Artichokes also improve quality of life for people suffering from dyspepsia and relieve their symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome [9] . Constipation, inflammation and other gastrointestinal issues are lessened.
3. Provides immunity from cardiovascular diseases
Artichokes have been subjected to extensive medical and herbal research and remedies. They have been known to demonstrate antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties [10] . People having high cholesterol content in their bodies stay at a greater risk of getting coronary attacks. It aids in the reduction of cholesterol in the system and thus prevents any possibilities of heart diseases.
Artichokes also promote better cardiovascular health by inducing lipidic and glycemic-reducing action [11] .
4. High in fibre content and assists in weight loss
Artichokes are a rich source of dietary fibre, which has a multitude of health benefits. High intakes of fibre lower the potential of heart diseases, strokes, hypertension, obesity and diabetes [12] . It lowers the serum cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Gastrointestinal problems like acid reflux, ulcers, haemorrhoids and constipation are relieved. Fibre intake makes us feel fuller, as it absorbs fluid inside the intestines and expands. Thus it enables hunger satisfaction for a longer time. We feel less obligated to grab snacks in between meals, maintain better energy levels, bloat lesser and thus lose weight gradually.
5. Prevents and controls diabetes
Diabetes can be mostly contributed to a sedentary lifestyle, high consumption of animal fats, fried items and less to zero physical activity. This worsens the insulin resistance within our body, thus causing hyperinsulinemia and finally diabetes [13] . Jerusalem artichokes are known to increase insulin sensitivity. It brings down the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides in the liver; it also lowers their level of circulation.
In addition to that, Jerusalem artichokes are high in fructooligosaccharides, which is an essential component in insulin resistance and exhibits antidiabetic effects [13] .
6. Cures anaemia and iron deficiency
Artichokes are a good source of plant-based iron. It is a handy option for calcium and iron intake for vegetarian people, who cannot gain the required iron from animal meat and eggs.
Iron deficiency can cause multiple functional impairments within our body. Our work capacity gets affected; we become more susceptible to diseases and our cognitive development slows down [14] .
Artichokes also contain good amounts of copper which help in the production of red blood cells. Iron acts as a carrier of oxygen within blood cells and transfers that to the lungs and tissues. Eating an artichoke every day is effective to combat anaemia.
7. Gives beautiful skin
Artichoke is a bundle of healthy vitamins and antioxidants. There is a deep connection between nutrition and skin health. Antioxidants like carotenoids, tocopherols, flavonoids, etc., along with vitamins (A, C, D and E) hold the capacity to enhance beauty [15] . Vitamin C helps with skin repair and pigmentation issues.
Vitamin E prohibits collagen cross-linking and peroxidation of lipids; it also helps with sunburned cells and UV skin damage. Vitamin A protects against UV rays, skin sags and wrinkles.
Antioxidants are helpful against skin damage and photodamage; they facilitate dead cell repairs, skin wrinkles and inflammation [16] .Also, as artichokes maintain good gut and liver health, they ensure that any toxins or pollutants are rejected. The skin infections and damages are easily repaired.
8. Improves brain functioning
Phosphorus and Vitamin C are found in good proportions in artichokes. Deficiencies of phosphorus have been known to cause a decline in cognitive abilities [17] . Besides, artichokes act as good vasodilators, which carries more oxygen to the brain for such functionality.
9. Enhances gall bladder health
Gall bladder acts as a facilitator for all other organs, thus having control over entire body health. Artichokes are excellent for bile production, thus strengthening gall bladder. It prevents accumulation of mineral deposits in kidneys, which can later turn to stones.
10. Improves bone health
Bones require other nutrients as well other than calcium for their better health. Artichokes contain an adequate amount of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, copper, magnesium and other antioxidants to improve bone density, and prevent conditions like osteoporosis. [18]

When To Buy Artichokes And Methods Of Preparation
An artichoke should look fresh, green and hydrated. It is better to buy when the petals are still closed, as it marks the freshness and tenderness of the vegetable. The leaves should give a little squeaky sound when pressed together. It is advisable to cut off the stem to avoid any spoilage; the vegetable should preferably be cooked within a week.
Artichoke should be rinsed well under cold water. It is usually covered in a thin film; hence it should be washed carefully. The stem should be cut; an inch or two from the top should be chopped off. It becomes easier now to pull apart the petals. A little seasoning with lemon juice prevents the browning of petals during cooking.
Steaming artichokes is very effective in the preservation of essential antioxidants and nutrients. The petals can be steeped in boiling water for half an hour. A clove of garlic, some ginger could add to its aroma. Many people boil them as well, on a high simmer for thirty minutes.
They can also be baked by seasoning them with spices and olive oil, wrapping them up in a few layers of foil. A temperature of 425 degrees Fahrenheit and an hour duration serves them just fine. Take care not to overcook or undercook the petals.
Precautions
Heavy consumption of artichoke can lead to loss of appetite and problems related to gall bladder and liver. People having allergies to marigold, chrysanthemum, daisies and similar plants that belong to the Asteraceae/ Compositae family, are much prone to having allergic reactions to the artichoke. The gall bladder stones can worsen due to bile duct obstruction and increased bile flow, caused by artichokes. Hence it is advisable not to consume this vegetable under such conditions.
- [1] Artichokes, (Globe or French). National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Legacy Release. United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service.
- [2] Salekzamani, S., Ebrahimi‐Mameghani, M., & Rezazadeh, K. (2018). The antioxidant activity of artichoke (Cynara scolymus): A systematic review and meta‐analysis of animal studies. Phytotherapy Research.
- [3] Pham-Huy, L. A., He, H., & Pham-Huy, C. (2008). Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. International Journal of Biomedical Science: IJBS, 4(2), 89-96.
- [4] Mileo, A. M., Di Venere, D., Abbruzzese, C., & Miccadei, S. (2015). Long term exposure to polyphenols of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) exerts induction of senescence driven growth arrest in the MDA-MB231 human breast cancer cell line. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015.
- [5] Metwally, N. S., Kholeif, T. E., Ghanem, K. Z., Farrag, A. R., Ammar, N. M., & Abdel-Hamid, A. H. (2011). The protective effects of fish oil and artichoke on hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 15(12), 1429-1444.
- [6] Horoszkiewicz, M., Kulza, M., Malinowska, K., Woźniak, A., Seńczuk-Przybyłowska, M., Wachowiak, A., & Florek, E. (2012). Artichoke-- the untapped potential of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis and liver diseases. Przeglad lekarski,69(10), 1129-1131.
- [7] Valdovska, A., Jemeljanovs, A., Pilmane, M., Zitare, I., Konosonoka, I. H., & Lazdins, M. (2014). Alternative for improving gut microbiota: use of Jerusalem artichoke and probiotics in diet of weaned piglets. Polish journal of veterinary sciences, 17(1), 61-69.
- [8] Rodriguez, T. S., Giménez, D. G., & De la Puerta Vázquez, R. (2002). Choleretic activity and biliary elimination of lipids and bile acids induced by an artichoke leaf extract in rats. Phytomedicine, 9(8), 687-693.
- [9] Bundy, R., Walker, A. F., Middleton, R. W., Marakis, G., & Booth, J. C. (2004). Artichoke leaf extract reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and improves quality of life in otherwise healthy volunteers suffering from concomitant dyspepsia: a subset analysis. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine, 10(4), 667-669.
- [10] Salem, M. B., Affes, H., Ksouda, K., Dhouibi, R., Sahnoun, Z., Hammami, S., & Zeghal, K. M. (2015). Pharmacological studies of artichoke leaf extract and their health benefits. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 70(4), 441-453.
- [11] Rondanelli, M., Monteferrario, F., Perna, S., Faliva, M. A., & Opizzi, A. (2015). Health-promoting properties of artichoke in preventing cardiovascular disease by its lipidic and glycemic-reducing action. Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease, 80(1).
- [12] Anderson, J. W., Baird, P., Davis, R. H., Ferreri, S., Knudtson, M., Koraym, A., ... & Williams, C. L. (2009). Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutrition Reviews, 67(4), 188-205.
- [13] Yang, H. J., Kwon, D. Y., Kim, M. J., Kang, S., Kim, D. S., & Park, S. (2012). Jerusalem artichoke and chungkookjang additively improve insulin secretion and sensitivity in diabetic rats. Nutrition & Metabolism, 9(1), 112
- [14] Abbaspour, N., Hurrell, R., & Kelishadi, R. (2014). Review on iron and its importance for human health. Journal of research in medical sciences : the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 19(2), 164-74.
- [15] Schagen, S. K., Zampeli, V. A., Makrantonaki, E., & Zouboulis, C. C. (2012). Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging. Dermato-Endocrinology, 4(3), 298-307.
- [16] Nguyen, G., & Torres, A. (2012). Systemic antioxidants and skin health. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: JDD, 11(9), e1-4.
- [17] Kerr, S.E. (1935). Studies on the phosphorus compounds of brain. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 110, 625-635.
- [18] Tucker, K. L., Hannan, M. T., Chen, H., Cupples, L. A., Wilson, P. W., & Kiel, D. P. (1999). Potassium, magnesium, and fruit and vegetable intakes are associated with greater bone mineral density in elderly men and women. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 69(4), 727-736.
-
 healthExclusive: Expert Shares Impact of Heat Waves on Infectious Disease Transmission
healthExclusive: Expert Shares Impact of Heat Waves on Infectious Disease Transmission -
 healthExclusive: Doctor Shares Why Women Should Prioritize Health, Key Resolutions For Well-being And Vitality
healthExclusive: Doctor Shares Why Women Should Prioritize Health, Key Resolutions For Well-being And Vitality -
 healthEverything You Need To Know About Deadly H5N1 Virus That Can Be 100 Times Worse That COVID-19 Pandemic
healthEverything You Need To Know About Deadly H5N1 Virus That Can Be 100 Times Worse That COVID-19 Pandemic -
 astrologyWorld Health Day 2024: Holistic Health Tips For 12 Zodiac Signs As Per Astrology
astrologyWorld Health Day 2024: Holistic Health Tips For 12 Zodiac Signs As Per Astrology -
 healthInstagram Claims Grapes Are Contaminated With Pesticides, Methods To Clean It Properly Before Consuming Them
healthInstagram Claims Grapes Are Contaminated With Pesticides, Methods To Clean It Properly Before Consuming Them -
 healthDutch Woman Opts For Euthanasia In May Not Due To Physical Illness, Know How To Build Mental Resiliance
healthDutch Woman Opts For Euthanasia In May Not Due To Physical Illness, Know How To Build Mental Resiliance -
 health20-Year-Old Man In China Suffers From Delusional Love Disorder, Know What Is Erotomania And Its Signs
health20-Year-Old Man In China Suffers From Delusional Love Disorder, Know What Is Erotomania And Its Signs -
 healthExclusive: On World Autism Day 2024, Let Us Empower Parents With Positive Strategies For Autism Care
healthExclusive: On World Autism Day 2024, Let Us Empower Parents With Positive Strategies For Autism Care -
 health10 Year Old Girl Dies After Eating Cake, How To Identify A Bad Cake Online, What Health Risks It Can Pose
health10 Year Old Girl Dies After Eating Cake, How To Identify A Bad Cake Online, What Health Risks It Can Pose -
 healthLove To Cuddle? These Are The 10 Amazing Health Benefits Of Cuddling Which Will Make You Want It More
healthLove To Cuddle? These Are The 10 Amazing Health Benefits Of Cuddling Which Will Make You Want It More -
 astrologyApril 2024 Health Horoscope: Know How This Month Will Affect Zodiac Signs In Terms Of Wellness
astrologyApril 2024 Health Horoscope: Know How This Month Will Affect Zodiac Signs In Terms Of Wellness -
 healthWhat Is iPhone Finger? Here's Why You Need To Worry About Its Negative Effects
healthWhat Is iPhone Finger? Here's Why You Need To Worry About Its Negative Effects


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



