Just In
- 6 hrs ago

- 7 hrs ago

- 11 hrs ago

- 12 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Sports
 CSK vs LSG Memes, IPL 2024: Fans Troll Chennai Super Kings as Marcus Stoinis Turns 'Hulk'
CSK vs LSG Memes, IPL 2024: Fans Troll Chennai Super Kings as Marcus Stoinis Turns 'Hulk' - News
 Senator Lambie Calls For Elon Musk's Imprisonment Over Wakeley Church Stabbing Posts
Senator Lambie Calls For Elon Musk's Imprisonment Over Wakeley Church Stabbing Posts - Movies
 Mirzapur 3 OTT Release Date, Platform: When Will Mirzapur Season 3 Premiere On Amazon Prime Video?
Mirzapur 3 OTT Release Date, Platform: When Will Mirzapur Season 3 Premiere On Amazon Prime Video? - Finance
 25% Dividend Record Date: Logistic Stock Nears 1-Year High And It Belongs To Mahindra; Motilal Neutral
25% Dividend Record Date: Logistic Stock Nears 1-Year High And It Belongs To Mahindra; Motilal Neutral - Education
 Telangana Inter Manabadi 1st and 2nd Year Results 2024 to be Declared Tomorrow
Telangana Inter Manabadi 1st and 2nd Year Results 2024 to be Declared Tomorrow - Automobiles
 Chrysler Pacifica Marks Seven Years As Most Awarded Minivan With New Campaign
Chrysler Pacifica Marks Seven Years As Most Awarded Minivan With New Campaign - Technology
 Xiaomi Robot Vacuum Cleaner S10, Handheld Garment Steamer, and Redmi Buds 5A Launched in India
Xiaomi Robot Vacuum Cleaner S10, Handheld Garment Steamer, and Redmi Buds 5A Launched in India - Travel
Kurnool's Hidden Gems: A Guide To Exploring India's Lesser-Known Treasures
Overdosing On Ginger Could Be Bad For People With These Medical Conditions
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is among the most commonly consumed spice or herb in the world. A bioactive compound named gingerol in 'the mighty ginger' has remarkable and evidence-based therapeutic properties against a range of health conditions such as diabetes, colds, stomach problems, hypertension, nausea and many others.

Despite the multiple health benefits of ginger, some studies say that consuming ginger, both in moderate and a large amounts, could be bad for people with certain health conditions. Find out which group of people should be aware of overdosing on ginger, and if you fall under these categories, you are advised to consult a medical expert for its proper dose to prevent any complications.


1. Pregnant
Ginger is helpful to alleviate nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. However, in a large amount, it could be harmful to pregnant women. The natural stimulants in ginger can lead to premature contractions. This may cause miscarriage or early delivery of the baby (pre-term labour). During pregnancy, overdosing on ginger must be avoided in any forms for women who are close to labour or have a history of bleeding disorders.
2. Underweight
Ginger is one of the best remedies for weight loss. Gingerol in ginger increases the rate of metabolism and suppresses appetite. Consumption of ginger causes calories to burn at a much higher rate and cause a person to eat less. Therefore, ginger must be avoided by people who want to gain weight or those who are already underweight.

3. Gallstones
A study has shown that ginger can increase the secretion of bile and cause the formation of gallbladder stones. Bile juice plays an important role in fat digestion and absorption; however, excessive consumption of ginger can stimulate the liver to produce more bile juice and accelerate the formation of gallbladder stones. [1]
4. Blood disorders
Ginger contains a salt named salicylates that acts as a pain-reliever, especially for people with osteoarthritis. [2] It also helps improve blood circulation and flow to the organs. However, people who are on blood-thinning or clotting medications, or those suffering from haemophilia, must avoid ginger as it may cause excessive bleeding.


5. Piles
Ginger can help reduce inflammation and pain in piles or haemorrhoids. But, according to some research and practice beliefs, ginger can cause irritation, itching, swell, discomfort and pain to people with piles. It may also encourage bleeding and make the condition worse.
6. Kidney
Ginger significantly possesses renoprotective effects due to its antioxidant activity. However, ginger contains a compound named ‘creatinine' and high levels of it in the blood, indicate severe kidney impairment such as chronic kidney disease.

7. GERD
For people with inflammatory conditions such as GERD (Acid reflux), the overdose of ginger (around four grams) in a single day can cause acid reflux, irritation of the stomach lining, chest pain and heartburn. To mention, moderate consumption of ginger is best to prevent the aforementioned complications of GERD.
8. Arthritis
In some people, ginger-based cream or gel for arthritis relief can worsen inflammation in people with arthritis. Ginger is an excellent pain reliever due to its anti-inflammatory properties, but in some, market-based ginger products or overconsumption of ginger can aggravate pain and inflammation of arthritis.

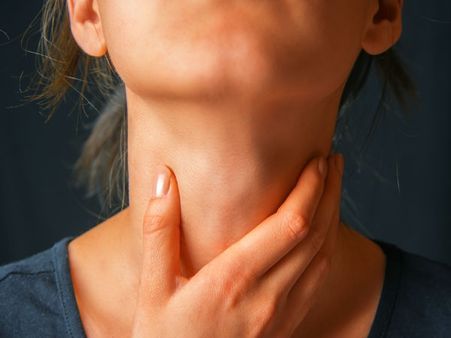
9. Thyroid
Though ginger is considered a safe herb, some studies reported ginger to cause side effects such as thyroiditis. The antioxidative and inhibitory effects of ginger on metabolic rate can damage the membranes that surround the thyroid hormones in follicles and release the hormone in the blood, leading to swelling or inflammation of the thyroid gland and its excessive production. [3]
10. Breastfeeding
Ginger is generally considered safe and effective for women who are breastfeeding. It is also known to increase the milk supply during the time. However, some beliefs say that overconsumption of ginger by breastfeeding mothers can sometimes trigger colic in babies, a condition characterised by intense crying with no apparent reason, unlike crying for a diaper change or hunger.

11. Depression
Gingerol in ginger is known to treat factors that could lead to anxiety or depression. However, in some cases, it may affect the release of serotonin, a happy hormone known for stabilising psychological conditions such as mood change, and cause depressive symptoms.
12. Cardiac arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias are referred to as a group of conditions that cause irregular heartbeats. Ginger is an excellent herb for many heart conditions, but in a large amount, can cause heart palpitations, if you are taking ginger with your heart medications.

Dosage
The dose of ginger varies for healthy adults, people with some medical conditions and the type of medical condition. For example, pregnant women are suggested to consume around 250 mg of ginger for four days (or up to 1 g) to reduce the symptoms of nausea and vomiting; people with gallbladder problems are recommended for less than 1200 mg, and people with osteoarthritis a dose between 170 mg to 340 mg, twice or thrice a day or as prescribed with certain medications.
The average dose of ginger is 0.5 g or 1 g, 3 or 4 times a day.
-
 healthWeight Loss: What Happens When You Drink Amla And Ginger Juice Once Every Week?
healthWeight Loss: What Happens When You Drink Amla And Ginger Juice Once Every Week? -
 healthWhat Happens When You Take Ginger Shots Every Day? Is It Healthy For Everyone?
healthWhat Happens When You Take Ginger Shots Every Day? Is It Healthy For Everyone? -
 healthMalaika Arora’s Ginger-Turmeric Cocktail For Summer Mornings
healthMalaika Arora’s Ginger-Turmeric Cocktail For Summer Mornings -
 wellnessDoes Ginger Improve Your Sex Drive? Is It Beneficial For Male Libido?
wellnessDoes Ginger Improve Your Sex Drive? Is It Beneficial For Male Libido? -
 wellnessSevere Period Pain? 3 Ways To Use Ginger For Immediate Relief From Menstrual Cramps
wellnessSevere Period Pain? 3 Ways To Use Ginger For Immediate Relief From Menstrual Cramps -
 wellnessHealth Benefits Of Mango Ginger And Its Uses: How Is It Different From Ginger?
wellnessHealth Benefits Of Mango Ginger And Its Uses: How Is It Different From Ginger? -
 disorders cureCOVID-19 And Blood Thinners: How Do They Help Increase Survival Rates In Critical COVID-19 Patients?
disorders cureCOVID-19 And Blood Thinners: How Do They Help Increase Survival Rates In Critical COVID-19 Patients? -
 wellness7 Healthy And Cooling Herbal Iced Teas For Summer With Recipes
wellness7 Healthy And Cooling Herbal Iced Teas For Summer With Recipes -
 wellnessGinger, Basil Tea, Clove Steaming And 31 Other Home Remedies For Headache
wellnessGinger, Basil Tea, Clove Steaming And 31 Other Home Remedies For Headache -
 diabetesCan Ginger Help Prevent And Manage Diabetes?
diabetesCan Ginger Help Prevent And Manage Diabetes? -
 hair care4 Brilliant Ways To Use Ginger Juice For Hair Growth
hair care4 Brilliant Ways To Use Ginger Juice For Hair Growth -
 wellness10 Home Remedies To Get Relief From Hernia
wellness10 Home Remedies To Get Relief From Hernia


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



