Just In
- 56 min ago

- 9 hrs ago

- 11 hrs ago

- 12 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Movies
 After Dalljiet Kaur-Nikhil Patel, Kundali Bhagya Star To DIVORCE Actress-Wife After 2 Yrs Of Marriage? DEETS
After Dalljiet Kaur-Nikhil Patel, Kundali Bhagya Star To DIVORCE Actress-Wife After 2 Yrs Of Marriage? DEETS - News
 Delhi Police Joins 'Look Between Your Keyboard' Trend, Gives Witty Driving Warning
Delhi Police Joins 'Look Between Your Keyboard' Trend, Gives Witty Driving Warning - Sports
 DC vs GT IPL 2024: Why Shubman Gill Held Back Spinner R Sai Kishore Till 19th over?
DC vs GT IPL 2024: Why Shubman Gill Held Back Spinner R Sai Kishore Till 19th over? - Travel
 Escape to Kalimpong, Gangtok, and Darjeeling with IRCTC's Tour Package; Check Itinerary
Escape to Kalimpong, Gangtok, and Darjeeling with IRCTC's Tour Package; Check Itinerary - Finance
 DCB Bank Q4 Results: PAT Grew 9% To Rs 156 Cr, NII Jumps 4.5%; Dividend Declared
DCB Bank Q4 Results: PAT Grew 9% To Rs 156 Cr, NII Jumps 4.5%; Dividend Declared - Technology
 OPPO Find X7 Ultra Camera Deep-Dive: Pushing the Boundaries of Photography on a Smartphone
OPPO Find X7 Ultra Camera Deep-Dive: Pushing the Boundaries of Photography on a Smartphone - Education
 MP Board Class 10th, 12th Results 2024, Know Alternative Ways to Check Your Result
MP Board Class 10th, 12th Results 2024, Know Alternative Ways to Check Your Result - Automobiles
 Aston Martin Vantage Launched In India At Rs 3.99 Crore
Aston Martin Vantage Launched In India At Rs 3.99 Crore
Carcinoid Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Carcinoid syndrome occurs when a carcinoid tumour, a rare cancerous tumour secretes certain chemicals into the bloodstream, causing an array of symptoms. The carcinoid tumours mostly appear in the lungs or gastrointestinal tract including your stomach, small intestine, colon, appendix, and rectum.

What Causes Carcinoid Syndrome? [1]
Carcinoid syndrome is caused when a carcinoid tumour releases hormonal chemical substances such as serotonin, bradykinins, tachykinins and prostaglandins into the bloodstream. Just a small percentage of carcinoid tumours secrete these chemicals, and the liver normally counteracts these chemicals before they have a chance to move throughout the body and cause symptoms.
However, when the tumour has advanced to the liver, the chemicals are released that aren't neutralized before reaching the bloodstream. People with carcinoid syndrome usually have an advanced carcinoid tumour.

Symptoms Of Carcinoid Syndrome [2]
- Skin turns pink, red, or purple colour
- Diarrhoea
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Facial skin lesions
- A sudden drop in blood pressure
Complications Of Carcinoid Syndrome [3]
- Carcinoid heart disease - People with carcinoid syndrome can also develop carcinoid heart disease. It is caused due to the thickening of the heart valves, making it difficult for them to function properly resulting in the leakage of the heart valves. The symptoms of carcinoid heart disease are fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Carcinoid crisis - It causes a severe episode of flushing, confusion, low blood pressure, and difficulty in breathing.
- Bowel obstruction - It occurs when the cancer spreads to the lymph nodes next to the small intestine, causing narrowing of the intestine and leading to bowel obstruction.
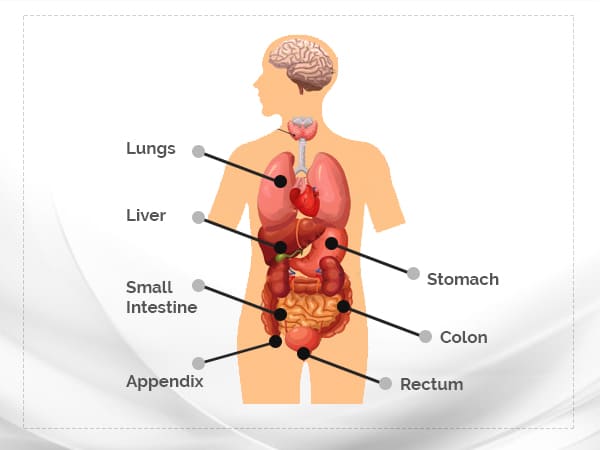
Diagnosis Of Carcinoid Syndrome [4]
The doctor will conduct a physical examination and may ask about your symptoms. He/she will then recommend further tests to confirm the diagnosis such as:
- Blood test - Your blood may contain certain substances, including the protein chromogranin A, which is released by some carcinoid tumours.
- Urine test - When your body breaks down extra serotonin, it creates an excess amount of a substance in the urine that indicates the body is processing extra serotonin.
- Imaging tests - Imaging tests like CT scan or MRI scan also detect the location of the primary carcinoid tumour and determine whether it has spread or not.
Treatment Of Carcinoid Syndrome [5]
- Medications
Medications in the form of injections are used to lower the signs and symptoms of carcinoid syndrome, including skin flushing and diarrhoea.
- Surgery
If the entire organ is infected with a carcinoid tumour, such as the appendix or the bowel, doctors may perform surgery. Also depending on where the tumour is, surgeons may also use an electric current to burn it off or cryosurgery to freeze it.
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs are used for the treatment of carcinoid tumours to shrink it.
- Biological therapy
Interferon alfa is an injectable medication which triggers the body's immune system to function better and slow down the growth of carcinoid tumours and relieves the symptoms.
- Radiation therapy
This kind of treatment kills the cancer cells and prevents them from multiplying.

- [1] Creutzfeldt, W., & Stöckmann, F. (1987). Carcinoids and carcinoid syndrome.The American journal of medicine,82(5), 4-16.
- [2] Gelhorn, H. L., Kulke, M. H., O’Dorisio, T., Yang, Q. M., Jackson, J., Jackson, S., ... & Lapuerta, P. (2016). Patient-reported symptom experiences in patients with carcinoid syndrome after participation in a study of telotristat etiprate: a qualitative interview approach.Clinical therapeutics,38(4), 759-768.
- [3] Mota, J. M., Sousa, L. G., & Riechelmann, R. P. (2016). Complications from carcinoid syndrome: review of the current evidence.Ecancermedicalscience,10, 662.
- [4] Halperin, D. M., Shen, C., Dasari, A., Xu, Y., Chu, Y., Zhou, S., … Yao, J. C. (2017). Frequency of carcinoid syndrome at neuroendocrine tumour diagnosis: a population-based study.The Lancet. Oncology,18(4), 525–534.
- [5] Moertel, C. G. (1983). Treatment of the carcinoid tumor and the malignant carcinoid syndrome.Journal of Clinical Oncology,1(11), 727-740.
-
 pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread?
pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread? -
 healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS? -
 healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy
health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy -
 pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby
pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby -
 healthStay Informed: The Hidden Dangers of Legionnaires' Disease and How to Prevent It
healthStay Informed: The Hidden Dangers of Legionnaires' Disease and How to Prevent It -
 healthMyths vs Facts: Can A Single Mosquito Bite Really Give You Dengue?
healthMyths vs Facts: Can A Single Mosquito Bite Really Give You Dengue? -
 healthTop 5 Reasons For Vaginal Rash: When You Should See A Doctor
healthTop 5 Reasons For Vaginal Rash: When You Should See A Doctor -
 healthCan Inhaling Menthol Help Improve Memory For Alzheimer's Disease?
healthCan Inhaling Menthol Help Improve Memory For Alzheimer's Disease? -
 healthWorld Vitiligo Day 2023: Are You At Risk Of Developing Vitiligo?
healthWorld Vitiligo Day 2023: Are You At Risk Of Developing Vitiligo? -
 beautyFather's Day 2023: Stretch Marks In Men, Causes And Treatments
beautyFather's Day 2023: Stretch Marks In Men, Causes And Treatments


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



