Just In
- 2 hrs ago

- 3 hrs ago

- 7 hrs ago

- 12 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Movies
 Anne Hathaway REVEALS 'Gross' Hollywood Audition Practices, Know What Bizarre Thing Happened With Oscar-Winner
Anne Hathaway REVEALS 'Gross' Hollywood Audition Practices, Know What Bizarre Thing Happened With Oscar-Winner - Finance
 1:1 Bonus Issue: Engineering Stock Turned Ex-Bonus On April 23, Hits New 52-Week High; Gives 268% Returns
1:1 Bonus Issue: Engineering Stock Turned Ex-Bonus On April 23, Hits New 52-Week High; Gives 268% Returns - Education
 Mizoram 10th Results to be declared Soon at mbse.edu.in, Check the Tentative Date
Mizoram 10th Results to be declared Soon at mbse.edu.in, Check the Tentative Date - News
 Not Hardik Pandya, Rohit Sharma Is Still Captain For Many Mumbai Indian Players: Irfan Pathan
Not Hardik Pandya, Rohit Sharma Is Still Captain For Many Mumbai Indian Players: Irfan Pathan - Technology
 Meta Quest OS is now Opened to Third-Party Hardware Manufacturers: Rebranded as Meta Horizon OS
Meta Quest OS is now Opened to Third-Party Hardware Manufacturers: Rebranded as Meta Horizon OS - Sports
 IPL 2024: 'Sunil takes offf the pressure from Me' - KKR star Phil Salt on dynamic partnership
IPL 2024: 'Sunil takes offf the pressure from Me' - KKR star Phil Salt on dynamic partnership - Automobiles
 Suzuki Access Electric To Electrify The Indian Scooter Market By 2024
Suzuki Access Electric To Electrify The Indian Scooter Market By 2024 - Travel
Kurnool's Hidden Gems: A Guide To Exploring India's Lesser-Known Treasures
Robotic Surgery – All You Need To Know
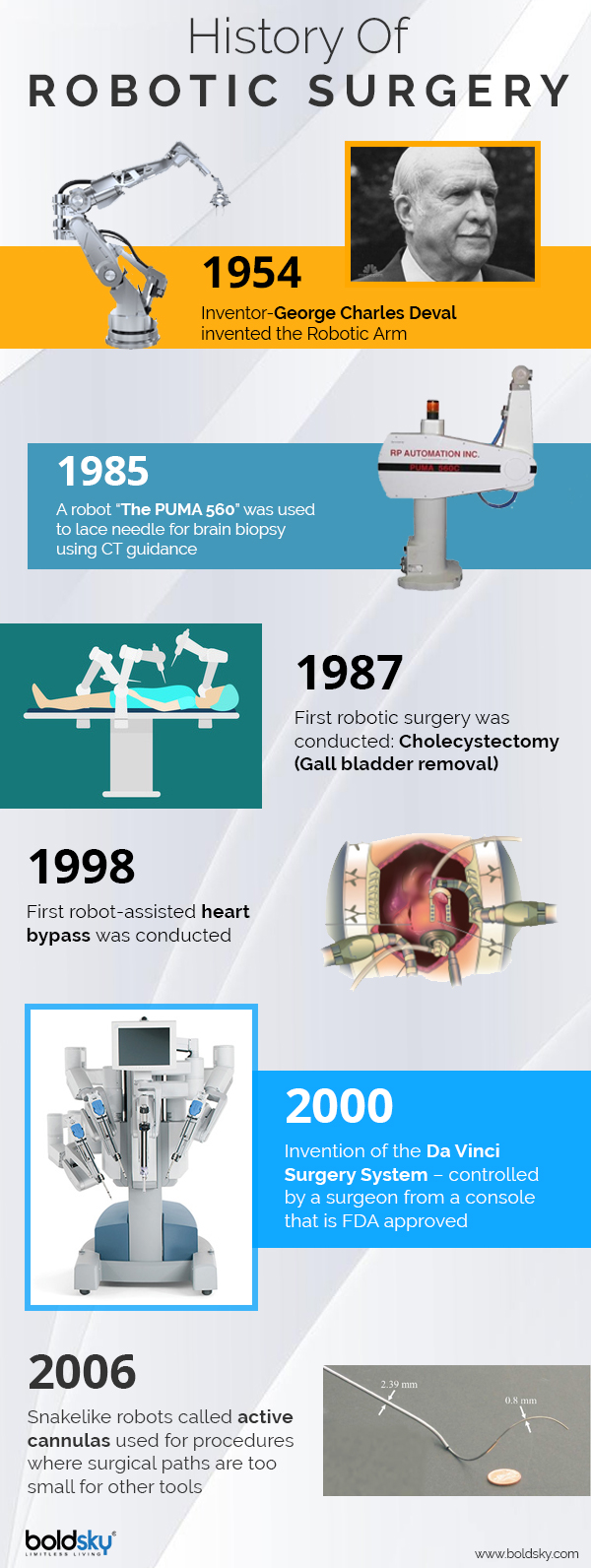
Patients today prefer operations based on minimal access technique over the traditional open surgery. This is because minimal invasive techniques lead to reduced postoperative pain, lower chances of wound infections, shorter hospital stays and better cosmetic outcomes. Favourable results also motivate researchers and surgeons to attempt minimal invasive surgical procedures whenever possible. Since the 1990s, the most used minimal invasive technique was laparoscopic procedures. However, certain limitations such as instability of video camera and a limited two-dimensional vision were some of the factors that made researchers think beyond laparoscopic measures when performing surgeries [1] .
These limitations of laparoscopic techniques were addressed by robotic surgery. This revolutionized minimal access surgery [2] . Extensive study and research are being conducted to make all forms of surgeries be possible, in the future, through robotics. Apart from the procedure itself, robotic surgery would create the need for a modification to the existing surgical training pattern. This would facilitate the reshaping of the learning curve of aspiring surgeons.
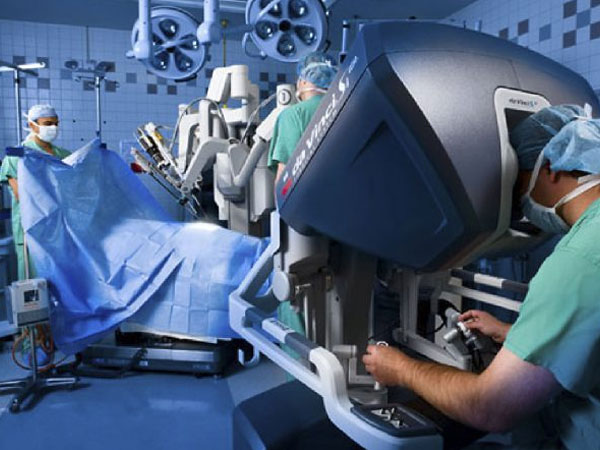
What Is Robotic Surgery?
A robot that is enabled to participate in the surgical process is said to be self-powered. It is a computer-controlled device that is programmed in such a manner that it aids the positioning and manipulation of surgical instruments. Such devices enable the surgeon to carry out tasks that are complex in nature [3] . These devices do not act independently (that is replacing human surgeons), but instead work as remote extensions that are governed by the surgeon-in-charge. The working of the robotic devices alongside the surgeon is quite often called 'master-slave manipulators' [4] .
Till date, there are two such master-slave robotic systems that have received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [5] :
1.
the
da
Vinci
Surgical
System
[6]
2.
the
ZEUS
system
[7]
The robotic systems have two basic components linked together with a computer using data cables [8] .
1. The surgeon's master console
The robot's user interface is the surgeon's master console. The master (surgeon) can attain the following information from the user interface [9] :
- View of the master manipulators - This has the handles/joysticks which helps a surgeon make surgical movements. These virtual movements are then translated into real-time surgical movements through the slave manipulators that are docked on the patient. Use of such manipulators make motion scaling [10] (large movements are converted into ultraprecise micromovements) and tremor filtering [11] possible. This facilitates the increase of precision and accuracy of the surgeon's movements.
- An endoscopic camera that is inside the patient's body controls the robot and provides a three-dimensional view of the surgical field. The gives a better and immersed view of the surgical field to the surgeon.
- The existing control panel helps with functions such as camera focusing, provision of accessory units and motion scaling.
2. Patient-side slave robotic manipulators [12]
Robotic arms are connected to the patient's body. These arms are designed to manipulate the surgical instruments and the camera with the help of the laparoscopic ports. The da Vinci system possesses micro articulations near the tip that handles surgical instruments. This is designed to duplicate the motions of the human wrist.
Advantages Of Robotic Surgery [13]
Compared with traditional techniques, many surgeons vouch for the attributes and ease of operation that robotic surgical procedures offer.
The following are some of the benefits of robotic surgery:
- Precision enhancement
- Improved flexibility and control during the surgery
- A better view of the surgical site
- Assists better performance of delicate and complex procedures (some of which are highly difficult using traditional methods)
- Reduced complication (surgical site infection)
- Minimal blood loss and reduced pain
- Less tissue damage
- Smaller scars that are less noticeable
- Quick recovery
Most Common Operations Performed Via Robotic Surgery [14]
The following is a list of the current fields that extensively observe robotic surgeries.
1. Robotic gastrointestinal surgery
- Heller's myotomy
- Gastrojejunostomy
- Antireflux operations
- Gastric bypass
- Esophagectomy
- Splenectomy
- Gastric banding colectomy
- Pancreatic resection
- Adrenalectomy
2. Robotic urologic surgery:
- Radical robotic prostatectomy is the most common type of robotic surgery.
3. Robotic gynecologic surgery:
- Salpingo-oophorectomy
- Microsurgical fallopian tube reanastomosis
- Hysterectomy
4. Robotic cardiothoracic surgery
- Robots allow complex cardiothoracic procedures such as
- mitral valve repairs,
- pericardiectomy, lobectomies,
- tumour enucleations, and
- atrial septal defect repair.
5. Robotic oncologic surgery
- Gastric cancer
- Colon cancer
- Retro mediastinal tumours
- Oesophageal tumours
- Thymoma
6. Robotic pediatric surgery
- Antireflux procedures for gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Pediatric congenital heart diseases
- Pyeloplasty for ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Limitations Of Robotic Surgery [15]
There are a few limitations that prevent robotic surgical techniques from achieving its complete potential. The following are some of the disadvantages of robotics in the field of surgical procedures:
-
Cost-effectiveness
The major issue lies with the costs involved in terms of purchasing the robot and its yearly maintenance. However, this aspect is believed to be sorted in the near future as robotic systems gain more acceptance. Also, a decrease in hospital stay and operative time will make robotic surgery cost-effective.
-
Bulky robotic equipment
Most of the present day robotic equipment is heavy and bulky making it difficult for the setup of the surgical procedure.
-
Lack of tactile feedback to the surgeon
Most of the time, the surgeon misses out on receiving tactile and force feedback from the robotic manipulators used. The ideal solution for this would be the use of haptics (systems designed to recreate the feeling of tissues via force feedback), which is likely to be the recognized solution in the near future.
Training Of Robotic Surgery To Medical Students
Surgical training has been following a more or less same structure for almost a century (at least until robotic surgery came into existence). Surgeons undergoing training had to gain operative experience through supervised trial and error methods on real patients. The cons of this approach would be compromising the patient's safety, prolonging surgical training and training dependent on the actual load of the case.
Robotic surgery has paved the path for acquiring surgical skills from means of simulating operations that can be done via a robot. Operations can be practised by using surgical robots. Simulations can be performed on three-dimensional, virtual-reality and soft-tissue models (which recreate the textures of human tissues through haptics) [16] .
Prior to operating on a patient, three-dimensional reconstructions of the anatomy of the patient under observation can be used to practice procedures and plan the operation. This is made possible through image-guided simulations. Telementoring [17] can be used to guide trainees during these simulations.
Using these techniques ensures that trainees acquire surgical skills sooner. This practice also helps in improving the safety of the patient by reducing the chances of surgical errors. The overall learning curve of the would-be surgeon is enhanced through robotic surgery training.
Is Robotic Surgery Right For You?
Robotic
surgery
for
specific
ailments
can
involve
risk,
quite
similar
to
the
conventional
open
surgeries.
It
is
therefore
essential
that
you
speak
out
and
clarify
the
pros
and
cons
of
robotic
surgery
with
your
healthcare
provider.
On
speaking
with
your
doctor,
you
might
be
surprised
to
hear
that
robotic
surgery
might
not
be
favourable
for
your
health
condition.
The
best
way
to
reach
a
conclusion
is
to
compare
this
technique
along
with
other
available
minimal
invasive
surgeries
and
if
the
traditional
open
surgery
would
be
a
better
alternative
[18]
.
Also,
robotic
surgery
might
only
be
available
in
sophisticated
hospitals.
[19]
How Costly Is Robotic Surgery In India? [19]
Robotic surgery still continues to be beyond the reach of most of the institutions and health-care system in India. The primary reason behind this is the excessive maintenance costs along with the disposable supply cost. On average, for regular procedures using robotic surgical methodologies, the ideal cost would be about Rs. 1.5 Lakh. Hospitals tend to charge more because of the high equipment cost associated with robotic surgery (which is about Rs. 15 Crore). Robotic surgeries are performed at esteemed hospitals across the country using the da Vinci robots.
On A Final Note...
Although still in its emerging spree, robotic surgery is surely one of the cutting-edge, finest development in the field of medical science. With proven far-reaching implications, robotic surgery ensures precision and dexterity improvement. This technology has allowed surgeons to perform surgeries that might not have been possible using traditional techniques.
Robotic surgery makes way for utmost patient safety and has shown several favourable outcomes. This technique allows minimal access surgery to be applicable to a wide range of procedures.
However, there is a need for controlled trials to identify the pros of robotic-assisted procedures alongside laparoscopic and other open techniques. The issues related to cost, clinical effectiveness and technical drawbacks need to be addressed [20] so that robotic procedures can be brought into the mainstream to reshape how surgical practice is conducted.
- [1] Morris B. (2005). Robotic surgery: applications, limitations, and impact on surgical education. MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine,7(3), 72.
- [2] Morris B. (2005). Robotic surgery: applications, limitations, and impact on surgical education.MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine,7(3), 72.
- [3] Stylopoulos, N., Rattner, D. Robotics and ergonomics.Surg Clin North Am.2003;83:1321–1337.
- [4] Gomez, G.Sabiston. Textbook of Surgery.17th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier Saunders; 2004. Emerging Technology in surgery: informatics, electronics, robotics.
- [5] Hashizume, M., Tsugawa, K. Robotic surgery and cancer: the present state, problems and future vision.Jpn J Clin Oncol.2004;34:227–237.
- [6] Ballantyne, G.H., Moll, F. The da Vinci telerobotic surgical system: the virtual operative field and telepresence surgery.Surg Clin North Am.2003;83:1293–1304.
- [7] Marescaux, J., Rubino, F. The ZEUS robotic system: experimental and clinical applications.Surg Clin North Am.2003;83:1305–1315.
- [8] Ballantyne, G.H. Robotic surgery, telerobotic surgery, telepresence, and telementoring. Review of early clinical results.Surg Endosc.2002;16:1389–1402.
- [9] Leung, T., & Vyas, D. (2014). Robotic Surgery: Applications.American journal of robotic surgery,1(1), 1-64.
- [10] Prasad, S.M., Prasad, S.M., Maniar, H.S., Chu, C., Schuessler, R.B., Damiano, R.J., Jr Surgical robotics: impact of motion scaling on task performance.J Am Coll Surg.2004;199:863–868.
- [11] Moorthy, K., Munz, Y., Dosis, A., et al. Dexterity enhancement with robotic surgery.Surg Endosc.2004;18:790–795.
- [12] Morris, B. (2005). Robotic surgery: applications, limitations, and impact on surgical education.MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine,7(3), 72.
- [13] Morris, B. (2005). Robotic surgery: applications, limitations, and impact on surgical education.MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine,7(3), 72.
- [14] Morris, B. (2005). Robotic surgery: applications, limitations, and impact on surgical education.MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine,7(3), 72.
- [15] Tan, Y., Liverneaux, P., & Wong, J. (2018). Current Limitations of Surgical Robotics in Reconstructive Plastic Microsurgery.Frontiers in surgery,5, 22.
- [16] Suzuki, S., Suzuki, N., Hayashibe, M., et al. Tele-surgical simulation system for training in the use of da Vinci surgery.Stud Health Technol Inform.2005;111:543–548.
- [17] Kaufmann, C., Rhee, P., Burris, D. Telepresence surgery system enhances medical student surgery training.Stud Health Technol Inform.1999;62:174–178.
- [18] Koh, D. H., Jang, W. S., Park, J. W., Ham, W. S., Han, W. K., Rha, K. H., & Choi, Y. D. (2018). Efficacy and Safety of Robotic Procedures Performed Using the da Vinci Robotic Surgical System at a Single Institute in Korea: Experience with 10000 Cases.Yonsei medical journal,59(8), 975-981.
- [19] Nelivigi G. G. (2007). Robotic surgery: India is not ready yet.Indian journal of urology : IJU : Journal of the Urological Society of India,23(3), 240-244.
- [20] Weiss, M. J., & Hogg, M. E. (2018). Robotic surgery: the future is now.Journal of visualized surgery,4, 30.
-
 healthExpert Article: Is Robotics Or Automation A Boon Or Bane To Both Doctors And Patients?
healthExpert Article: Is Robotics Or Automation A Boon Or Bane To Both Doctors And Patients? -
 healthDoctors Day: The Future of Medicine in India: Top 5 Recent Medical Innovations
healthDoctors Day: The Future of Medicine in India: Top 5 Recent Medical Innovations -
 healthBypass Surgery: When Is It Necessary? Is It Required For People With Severe Chest Pain?
healthBypass Surgery: When Is It Necessary? Is It Required For People With Severe Chest Pain? -
 disorders cureNew Treatment For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Could Provide Lasting Relief Without Surgery
disorders cureNew Treatment For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Could Provide Lasting Relief Without Surgery -
 wellnessExpert Article: CUVIS Joint, Your Robotic Doctor: World's First Active Robotic Knee Replacement System
wellnessExpert Article: CUVIS Joint, Your Robotic Doctor: World's First Active Robotic Knee Replacement System -
 healthNational Plastic Surgery Day 2022: Microsurgical Techniques For Attaching Amputated Fingers
healthNational Plastic Surgery Day 2022: Microsurgical Techniques For Attaching Amputated Fingers -
 wellnessFirst Hospital In South India To Use Sentinel Device To Reduce Risk Of Stroke During Heart Valve Implantation
wellnessFirst Hospital In South India To Use Sentinel Device To Reduce Risk Of Stroke During Heart Valve Implantation -
 wellnessApollo Hospitals Successfully Performs Surgery To Remove Rare Recurrent Chest Wall Tumour
wellnessApollo Hospitals Successfully Performs Surgery To Remove Rare Recurrent Chest Wall Tumour -
 disorders cureFirst Patient Who Received Pig Heart Transplant Dies After Two Months
disorders cureFirst Patient Who Received Pig Heart Transplant Dies After Two Months -
 kidsJaw Bone Surgery: Hospital Successfully Treats And Restores 8-Year-Old Child's Ability To Open Her Mouth
kidsJaw Bone Surgery: Hospital Successfully Treats And Restores 8-Year-Old Child's Ability To Open Her Mouth -
 healthCancer Tumour In Man's Face Removed In 'Scarless Surgery' At Delhi Hospital
healthCancer Tumour In Man's Face Removed In 'Scarless Surgery' At Delhi Hospital -
 disorders cureExpert Article: Breast Conservation Surgery - The New Paradigm
disorders cureExpert Article: Breast Conservation Surgery - The New Paradigm


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



