Just In
- 3 hrs ago

- 4 hrs ago

- 8 hrs ago

- 12 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- News
 Electoral Bonds Controversy: Amit Shah Slams Rahul Gandhi, Asks Opposition Too Got Money, Is It Extortion?
Electoral Bonds Controversy: Amit Shah Slams Rahul Gandhi, Asks Opposition Too Got Money, Is It Extortion? - Movies
 Main Ladega, Mary Kom, Toofan - 5 Bollywood Boxing Dramas You Need To Watch
Main Ladega, Mary Kom, Toofan - 5 Bollywood Boxing Dramas You Need To Watch - Finance
 1:5 Stock Split: PSU Bank Fixes Record Date For First Ever Stock Split; Buy For Rs 650-680 Targets
1:5 Stock Split: PSU Bank Fixes Record Date For First Ever Stock Split; Buy For Rs 650-680 Targets - Sports
 T20 World Cup: 'He will definitely be in my list' - Anjum Chopra handpicks 2 wicketkeeper-batters for India squad
T20 World Cup: 'He will definitely be in my list' - Anjum Chopra handpicks 2 wicketkeeper-batters for India squad - Automobiles
 Tata Motors To Manufacture Jaguar Land Rover Cars In Billion Dollar TN Plant - Report
Tata Motors To Manufacture Jaguar Land Rover Cars In Billion Dollar TN Plant - Report - Technology
 OnePlus Ace 3 Pro Leak Hints at New Design; Expected Launch, Specifications We Know So Far
OnePlus Ace 3 Pro Leak Hints at New Design; Expected Launch, Specifications We Know So Far - Travel
 Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions
Journey From Delhi To Ooty: Top Transport Options And Attractions - Education
 IIIT-Bangalore Introduces PG Diploma In Digital Product Design And Management
IIIT-Bangalore Introduces PG Diploma In Digital Product Design And Management
World Leprosy Eradication Day 2021: Types, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
Every year, World Leprosy Eradication Day is observed on the last Sunday of the month of January, that is January 31 this year (2021). But in India, World Leprosy Eradication Day is observed on 30 January. The day aims to raise awareness on the prevalence and severity of Leprosy, a disease that is often believed to be extinct.

The theme of the World Leprosy Eradication Day 2021 campaign is Beat Leprosy, End Stigma and Advocate for Mental Well-Being. The theme was developed with the aim to elevate the level of care and attention people with leprosy receive; reports point out that it is not only the disease that is overlooked but also those affected by it.
In 2020, BIREME/PAHO/WHO developed and launched the World Leprosy Day Window of Knowledge, in partnership with the Regional Leprosy Program, which contains information for health professionals, researchers and the general public.
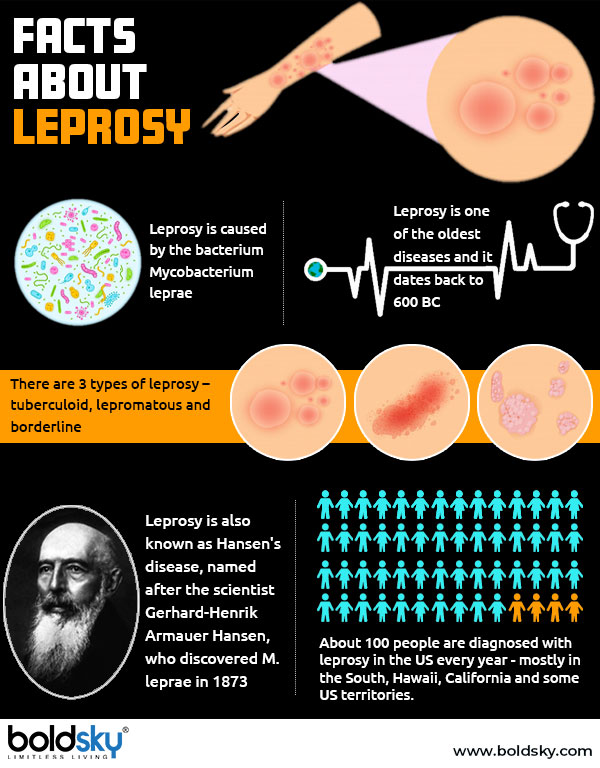
Leprosy is an infectious chronic disease that usually targets the nervous system, especially the feet, hands, and face. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. Leprosy is also known as Hansen's disease.
According to the WHO report, the global prevalence at the end of 2016 was 171, 948 with a prevalence rate of 0.23 per 10,000 population [1] . Worldwide, 210,000 new cases are reported annually, of which 15,000 are children.
Leprosy disease spreads through contact with the mucous secretions of a person infected with leprosy. It usually happens when a person sneezes or coughs. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the disease has an average incubation period of five years.
Types Of Leprosy [2]
- Tuberculoid leprosy - It is a mild, less severe form of leprosy which causes few patches of pale-coloured skin. The skin may feel numb because of the damaged nerve underneath.
- Lepromatous leprosy - This type of leprosy affects the nerves, skin, and other organs. Lepromatous leprosy is more contagious.
- Borderline leprosy - This form of leprosy shows the features of both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. It is also characterised by numerous asymmetrical lesions.
Leprosy spreads through contact with the mucosal secretions of a person with the infection and usually occurs when a person with leprosy sneezes or coughs. The disease is not highly contagious. However, close, and continuous contact with an untreated person for a longer period of time can lead to contracting leprosy.

Symptoms Of Leprosy
- Skin lesions
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness in the hands, arms, legs and feet
- Loss of eyebrows or eyelashes
- Dry or thick skin
- Painless ulcers on the soles of feet
- Painless swelling or lumps on the face
- Discoloured patches of skin
- Enlarged nerves
Complications Of Leprosy
- Hair loss
- Muscle weakness
- Disfigurement
- Inability to use hands and feet
- Iritis, an inflammation of the iris in the eye
- Blindness
- Erectile dysfunction
- Infertility
- Permanent nerve damage in the legs and arms
- Glaucoma
- Chronic nasal congestion and nosebleeds
- Kidney failure
Diagnosis Of Leprosy [3]
A physical examination will be conducted by the doctor and a biopsy is also done by removing a small piece of skin or nerve and is sent to the laboratory for testing.
The doctor may also perform a lepromin skin test to determine the form of leprosy by injecting a small amount of inactivated leprosy-causing bacterium into the upper forearm.
A person with tuberculoid or borderline leprosy will yield positive results at the site of the injection.

Treatment of Leprosy [4]
In 1995, WHO developed a multidrug therapy to cure all types of leprosy. In addition, several antibiotics are used to treat leprosy by killing the bacteria that cause it. These antibiotics are dapsone, clofazimine, minocycline, ofloxacin, and rifampin.
Anti-inflammatory medicines are used for leprosy treatment to control nerve pain and damage. These medicines include aspirin, thalidomide, or prednisone.
The treatment for leprosy could last for months or up to 1 to 2 years.
How To Prevent Leprosy
Avoid long-term, close contact with an untreated person (infected) with leprosy.
On A Final Note...
Leprosy is found in 127 countries, with 80 per cent of cases in India, Brazil and Indonesia. People affected by leprosy are often discriminated against and stigmatized, which has a negative impact on their access to diagnosis, the result of treatment and the result of care.
- [1] Rao, P. N., & Suneetha, S. (2018). Current Situation of Leprosy in India and its Future Implications.Indian dermatology online journal,9(2), 83–89.
- [2] Thakkar, S., & Patel, S. V. (2014). Clinical profile of leprosy patients: a prospective study.Indian journal of dermatology,59(2), 158–162.
- [3] Sengupta, U. (2019). Recent laboratory advances in diagnostics and monitoring response to treatment in leprosy.Indian dermatology online journal,10(2), 106.
- [4] Lastória, J. C., & Abreu, M. A. (2014). Leprosy: review of the epidemiological, clinical, and etiopathogenic aspects - part 1.Anais brasileiros de dermatologia,89(2), 205–218.
-
 disorders cureWorld Leprosy Day 2021: Facts You Might Not Know About Leprosy
disorders cureWorld Leprosy Day 2021: Facts You Might Not Know About Leprosy -
 disorders cureMadarosis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
disorders cureMadarosis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment -
 disorders cureMesothelioma: The Most Dangerous Cancer To Grip Your Breath!
disorders cureMesothelioma: The Most Dangerous Cancer To Grip Your Breath! -
 prenatalEndoscopic Surgery
prenatalEndoscopic Surgery -
 insyncB'day Of Rahul Celebrated In Pondy
insyncB'day Of Rahul Celebrated In Pondy -
 healthHow You Blink Per Minute Can Determine If You Have An Underlying Health Condiion, Here's What You Need To Know
healthHow You Blink Per Minute Can Determine If You Have An Underlying Health Condiion, Here's What You Need To Know -
 healthWhat Is Parrot Fever? 5 Dies In Europe Due To This Outbreak, Everything You Need To Know
healthWhat Is Parrot Fever? 5 Dies In Europe Due To This Outbreak, Everything You Need To Know -
 healthPreventing Dementia, Diabetes, And Heart Disease May Lie In Your Oral Health Habits
healthPreventing Dementia, Diabetes, And Heart Disease May Lie In Your Oral Health Habits -
 healthWhat Is Zombie Deer Disease? What Scientists Want You To Know About Its Transmission To Humans
healthWhat Is Zombie Deer Disease? What Scientists Want You To Know About Its Transmission To Humans -
 healthMeasles Outbreak In MP: Causes, Symptoms, How Parents Can Keep Children Safe By Taking Necessary Precautions
healthMeasles Outbreak In MP: Causes, Symptoms, How Parents Can Keep Children Safe By Taking Necessary Precautions -
 healthFarmer’s Protest: Farmers Face Tear Gas At Shambhu Border, How This Riot Control Agent Can Affect Human Body
healthFarmer’s Protest: Farmers Face Tear Gas At Shambhu Border, How This Riot Control Agent Can Affect Human Body -
 healthWhat Happens If You Eat Food That Has A Fly On It? Knowing The Reasons Will Make You Reconsider Outdoor Snack
healthWhat Happens If You Eat Food That Has A Fly On It? Knowing The Reasons Will Make You Reconsider Outdoor Snack


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



