Just In
- 7 hrs ago

- 8 hrs ago

- 9 hrs ago

- 9 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Finance
 7:1 Bonus, 1:10 Split: At Rs 3.5, NBFC Penny Stock Hits Back-To-Back Lower Circuits; Big Announcement Soon
7:1 Bonus, 1:10 Split: At Rs 3.5, NBFC Penny Stock Hits Back-To-Back Lower Circuits; Big Announcement Soon - Movies
 EXCLUSIVE Interview! Alankrita Sahai On Journey From Beauty Pageant Winner To Films, Nepotism In Bollywood
EXCLUSIVE Interview! Alankrita Sahai On Journey From Beauty Pageant Winner To Films, Nepotism In Bollywood - News
 EVM VVPAT Vote Cross-Checking Case: Can't Count 60 Crore Slips: Supreme Court; Next Hearing On Thursday
EVM VVPAT Vote Cross-Checking Case: Can't Count 60 Crore Slips: Supreme Court; Next Hearing On Thursday - Sports
 KKR vs RR, IPL 2024 Twitter Reaction: Sunil Narine hailed by Social Media after Stellar Century
KKR vs RR, IPL 2024 Twitter Reaction: Sunil Narine hailed by Social Media after Stellar Century - Education
 UPSC CDS 1 Exam on 21 April 2024
UPSC CDS 1 Exam on 21 April 2024 - Automobiles
 Jeep Compass Gets More Powerful 268.3bhp Turbo Petrol Engine – Check Out All The Details Here
Jeep Compass Gets More Powerful 268.3bhp Turbo Petrol Engine – Check Out All The Details Here - Technology
 Redmi Pad SE With 90Hz Display Launching on April 23 in India; Could Be Priced for Less Than Rs 20,000
Redmi Pad SE With 90Hz Display Launching on April 23 in India; Could Be Priced for Less Than Rs 20,000 - Travel
 From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
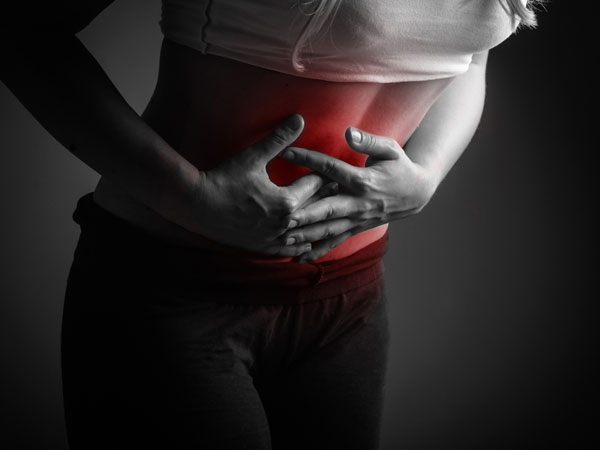
Appendicitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Severe pain in the lower right-hand side of the abdomen can be a symptom of appendicitis. Most of the times, appendicitis is a medical emergency and requires surgical treatment to avoid complications.
What Is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch-like tissue projecting from your colon or large intestine on the right side of your abdomen. This causes severe pain and most often occurs in people between the ages of 10 and 30. Appendicitis can be acute or chronic [1] , [2] .
What Causes Appendicitis
Appendicitis occurs when there is a blockage in the lining of the appendix, resulting in infection due to the multiplying of bacteria, causing the appendix to become inflamed, swollen and filled with pus.
A build-up of hardened stool, tumours, intestinal worms, a traumatic injury or enlarged lymphoid follicles are some of the ways in which your appendix can get blocked.
Symptoms Of Appendicitis
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal bloating
- Fever
- Constipation or diarrhoea
- Sudden pain on the right side of your lower abdomen
- Sudden pain that begins around your navel and shifts to the lower abdomen
- Painful urination
Risk Factors Of Appendicitis [3]
- Age - Appendicitis most often affects people between the ages of 15 and 30 years old.
- Sex - Appendicitis is common in males than females.
- Family history - People who have a family history of appendicitis have a higher risk.

Complications Of Appendicitis [4]
Peritonitis - When the appendix ruptures and spreads the infection into the abdomen, it is called peritonitis. This causes bowel movements to shut down.
Abscess - If your appendix bursts, you may develop an abscess. If the abscess isn't treated, it can cause peritonitis.
Diagnosis Of Appendicitis [5]
The symptoms of appendicitis are similar to other health conditions like urinary tract infection, gastritis, intestinal infection, gallbladder problems, and ovary problems. So, diagnosing appendicitis can be difficult.
The tests which are used to diagnose appendicitis are a blood test, urine test, physical examination, and imaging tests.
Treatment Of Appendicitis [6]
Appendectomy (Surgery to remove the appendix)
The surgery is normally performed using 3 small incisions (each ¼ to ½ inch) known as laparoscopy. During the laparoscopy, the surgeon inserts special surgical tools and a video camera inside the abdomen to remove the appendix.
This surgery helps you recover faster and you may return to normal activities in 2 to 3 weeks. Strenuous activity can be done within 4 to 6 weeks.
If your appendix has ruptured and the infection has spread to other parts of the abdomen, you may require an open appendectomy, which allows the surgeon to clean the abdominal activity. In this case, you will have to spend more time in the hospital to recover.

Lifestyle Changes To Recover Faster From Appendicitis
- Avoid strenuous activity for 10 to 14 days
- Sleep when you feel tired
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Go for a gentle walk every day
Prevention Of Appendicitis
One can't prevent appendicitis, but you can include high-fibre foods into your diet to lower the risk of appendicitis.
- [1] Sartelli, M., Baiocchi, G. L., Di Saverio, S., Ferrara, F., Labricciosa, F. M., Ansaloni, L., ... & Agboola, J. (2018). Prospective observational study on acute appendicitis worldwide (POSAW).World Journal of Emergency Surgery,13(1), 19.
- [2] Crabbe, M. M., Norwood, S. H., Robertson, H. D., & Silva, J. S. (1986). Recurrent and chronic appendicitis.Surgery, gynecology & obstetrics,163(1), 11-13.
- [3] Tantarattanapong, S., & Arwae, N. (2018). Risk factors associated with perforated acute appendicitis in geriatric emergency patients.Open access emergency medicine : OAEM,10, 129–134.
- [4] IAMARINO, A. P., Juliano, Y., ROSA, O., Novo, N. F., FAVARO, M. D. L., JÚNIOR, R., & FONTENELLE, M. A. (2017). Risk factors associated with complications of acute appendicitis.Revista do Colégio Brasileiro de Cirurgiões,44(6), 560-566.
- [5] Puylaert, J. B., Rutgers, P. H., Lalisang, R. I., de Vries, B. C., van der Werf, S. D., Dörr, J. P., & Blok, R. A. (1987). A prospective study of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of appendicitis.New England Journal of Medicine,317(11), 666-669.
- [6] Prystowsky, J. B., Pugh, C. M., & Nagle, A. P. (2005). Appendicitis.Current problems in surgery,42(10), 694-742.
-
 disorders cure10 Warnings Signs Your Appendix Might Burst
disorders cure10 Warnings Signs Your Appendix Might Burst -
 disorders cure14 Natural Remedies To Treat Appendicitis
disorders cure14 Natural Remedies To Treat Appendicitis -
 nutritionTomato Seeds: Benefits And Side Effects
nutritionTomato Seeds: Benefits And Side Effects -
 disorders cureIf You Are Having Appendicitis Pain, Try These 8 Foods To Get Relief
disorders cureIf You Are Having Appendicitis Pain, Try These 8 Foods To Get Relief -
 wellnessSuffering From Appendicitis? Choose The Right Foods And Leave Out The Rest
wellnessSuffering From Appendicitis? Choose The Right Foods And Leave Out The Rest -
 sathya sai babaSathya Saibaba Performs A Miraculous Surgery
sathya sai babaSathya Saibaba Performs A Miraculous Surgery -
 pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread?
pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread? -
 healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS? -
 healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy
health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy -
 pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby
pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



