Just In
- 3 hrs ago

- 3 hrs ago

- 4 hrs ago

- 5 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- News
 IPL 2024 KKR vs RR Dream11 Match Prediction Today: Best Players, Team, Stats For Kolkata vs Rajasthan Match
IPL 2024 KKR vs RR Dream11 Match Prediction Today: Best Players, Team, Stats For Kolkata vs Rajasthan Match - Movies
 Varshangalkku Shesham Review By Mohanlal: A Heartfelt Reflection On Nostalgia And Life's Journeys
Varshangalkku Shesham Review By Mohanlal: A Heartfelt Reflection On Nostalgia And Life's Journeys - Automobiles
 Raptee Energy Marks A New Era In EV With First Electric Motorcycle Launch
Raptee Energy Marks A New Era In EV With First Electric Motorcycle Launch - Finance
 CRISIL March 2024 Quarter Sees 5.51% Net Profit Drop; Dividend Announced
CRISIL March 2024 Quarter Sees 5.51% Net Profit Drop; Dividend Announced - Sports
 ICC Women's ODI Batting Rankings: Laura Wolvaardt overtakes Ellyse Perry to climb into top 5; Smriti Mandhana holds firm at No. 4
ICC Women's ODI Batting Rankings: Laura Wolvaardt overtakes Ellyse Perry to climb into top 5; Smriti Mandhana holds firm at No. 4 - Technology
 Garena Free Fire Max Redeem Codes for April 16: Get Access to the Latest In-game Loot
Garena Free Fire Max Redeem Codes for April 16: Get Access to the Latest In-game Loot - Education
 UPSC CSE Result 2023 Declared, Check the Full List of Selected Candidates Here
UPSC CSE Result 2023 Declared, Check the Full List of Selected Candidates Here - Travel
 From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
15 Surprising Health Benefits Of Amla (Indian Gooseberry)
Indian gooseberry, also known as amla, is mostly eaten to ward away cough and cold and promote hair growth. But this fruit does much more than that and therefore, simply eating it either in raw or dried form will work wonders for your health.
In Ayurvedic medicine, amla has been used to prevent common diseases and amla juice is known to balance the three doshas - vata, kapha and pitta. Amla regenerates all the tissues in the body and builds ojas, the essence of immunity and youthfulness [1] .

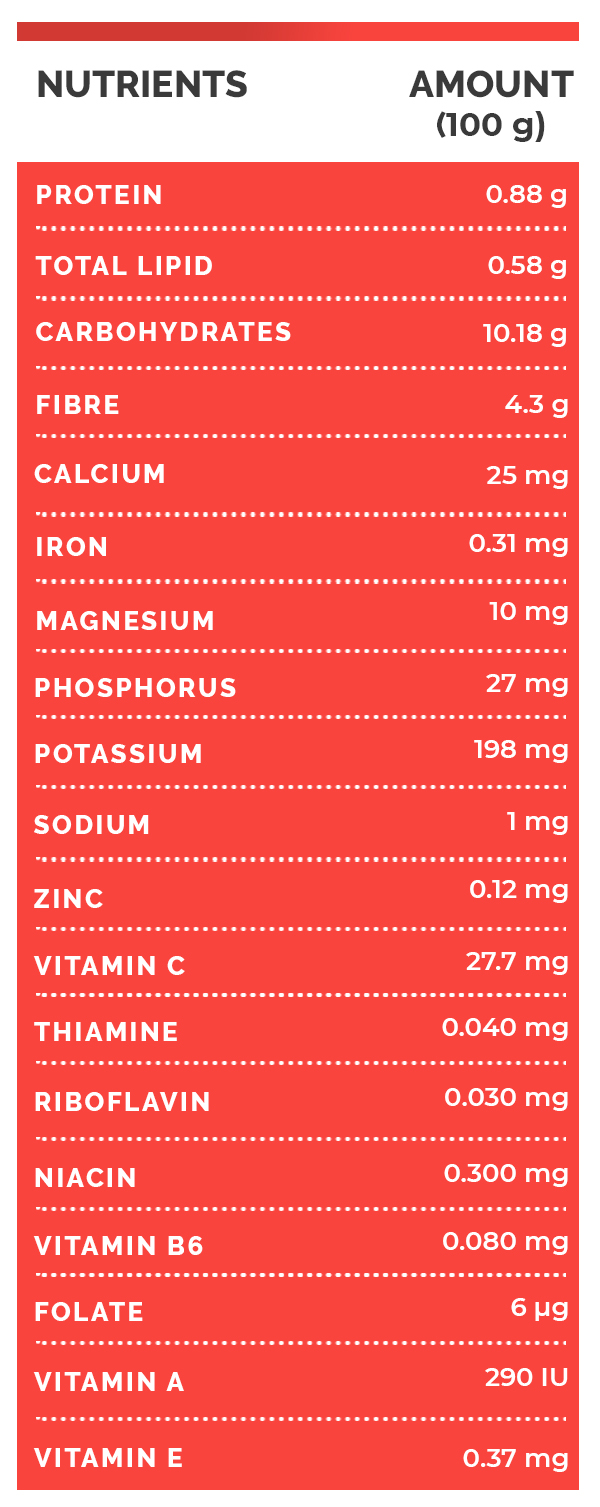
Nutrition Value Of Amla (Indian Gooseberry)
100 g of amla contain 87.87 g water and 44 kcal (energy). They also contain
- 0.88 g protein
- 0.58 g total lipid (fat)
- 10.18 g carbohydrate
- 4.3 g total dietary fibre
- 25 mg calcium
- 0.31 mg iron
- 10 mg magnesium
- 27 mg phosphorus
- 198 mg potassium
- 1 mg sodium
- 0.12 mg zinc
- 27.7 mg vitamin C
- 0.040 mg thiamine
- 0.030 mg riboflavin
- 0.300 mg niacin
- 0.080 mg vitamin B6
- 6 µg folate
- 290 IU vitamin A
- 0.37 mg vitamin E
Health Benefits Of Amla (Indian Gooseberry)
1. Aids in detoxification
Amla is rich in antioxidants that help in eliminating the toxins while nourishing and protecting the body's natural defence system. Amla juice is usually prescribed to be consumed on an empty stomach in the morning to detoxify the body. But, make sure you don't drink too much of it as it may cause acidity due to the vitamin C content.
2. Promotes liver health
The liver plays an important function in removing the excess waste and toxins from the body. In order to maintain the proper functioning of the liver, it is essential to consume amla as it is known to have hepatoprotective properties which prevent liver damage. Amla prevents the toxic effects of hepatotoxic agents like ethanol, paracetamol, carbon tetrachloride, heavy metals, ochratoxins, etc. [2] .
3. Aids in weight loss
Amla contains a good amount of fibre that keeps you full and satisfied after consumption. It increases the metabolic rate, which is determined by how fast your body burns calories. This leads to rapid loss of weight, high energy levels and increased lean muscle mass [3] .
4. Prevents struvite stones
Struvite stones are caused by bacterial infections that break down urea to ammonium and raise the pH of urine to neutral or alkaline values. These stones occur in the urinary system of humans, particularly women. A study showed that consuming amla could reduce nucleation of struvite crystals [4] . Amla also prevents the formation of gallbladder stones.
5. Treats jaundice
Jaundice occurs when there is a build-up of bilirubin, a waste material created by the breakdown of dead red blood cells in the liver. The therapeutic properties of amla could reduce the effect of jaundice and is widely used in Ayurvedic medicine for the treatment of jaundice [5] .
6. Enhances heart-health
Amla can reduce the risk of heart disease and build-up of plaque by lowering cholesterol levels in the blood. According to a study published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, eating amla for 28 days significantly reduced cholesterol levels [6] . Another study showed that amla increased good cholesterol and reduced blood pressure [7] .
7. Helps in digestion
According to Ayurveda, amla improves appetite and ignites the digestive fire, both of which are important for healthy digestion. A study found that amla extract stopped the development of stomach lesions, gastric ulcers and protected the stomach from injury [8] . Eating amla or consuming the juice after a meal will help improve your digestion.
8. Supports cognitive function
Neurodegenerative diseases occur as a result of the progressive degeneration of nerve cells. Research has shown that Indian gooseberry has a positive effect on brain function. A study done in 2016 showed that gooseberry extract has the potential to elevate memory retention and antioxidant levels. It also decreased the levels of acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme linked to Alzheimer's disease [9] .
9. Prevents constipation
Amla can help prevent constipation due to its laxative properties and fibre content. This promotes bowel regularity and prevents constipation. When fibre passes through the digestive system, it adds bulk to the stool and help in easing its passage, thereby preventing constipation [10] .
10. Inhibits cancer
Amla has anti-cancerous properties. A 2005 study showed that gooseberry extract can decrease skin cancer by 60 per cent [11] . Other studies have also shown that the presence of phytochemicals and antioxidants could stop the growth of lung, colon, liver, breast and ovarian cancer cells [12] , [13] .
11. Boosts the immune system
Amla has vitamin C, an antioxidant, which fights against the free radicals that damage the immune system. Consumption of amla and amla juice can effectively treat cold, cough and sore throat by enhancing the function of natural killer cells (NK cells), lymphocytes and neutrophils [14] .
12. Lowers pain and inflammation
Inflammation is the root cause of most chronic diseases and conditions such as arthritis, diabetes and cancer. According to a study, gooseberry extract lowered the levels of pro-inflammatory markers in human cells due to the presence of antioxidants [15] .
13. Controls diabetes
The antioxidants and fibre in gooseberries help in regulating normal blood sugar levels. Fibre works by slowing the absorption of sugar in the bloodstream and prevents a spike in blood sugar level. This reduces the risk of diabetes and complications associated with it [16] .
14. Strengthens bones
Amla is known to lower the risk of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis as it is rich in calcium content. Calcium is required for building stronger bones and if you are calcium deficient, your bones and teeth start deteriorating, leading to the loss of bone mineral density [17] .
15. Promotes skin and hair health
Amla contains antioxidants which reverse ageing and reduce skin cell damage. A study found that amla extract raises the production of collagen, a protein responsible for providing youthfulness and elasticity to the skin [18]. Amla also helps trigger hair growth, prevents hair fall and strengthens root of the hair due to its rich source of vitamin E and proteins [19] .
Ways To Eat Amla (Indian Gooseberry)
- Chop the amla and have it with some salt for a tasty snack.
- Cut the washed amla and dry them in the sun. Then toss the dried amla in lemon juice and salt.
- You can also consume amla juice.
- Amla is also used for making amla chutney, amla pickle, etc.
How Much Amla To Eat In A Day
Two to three amla can be consumed in a day.
- [1] Pole, S. (2006).Ayurvedic medicine: The principles of traditional practice. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- [2] Thilakchand, K. R., Mathai, R. T., Simon, P., Ravi, R. T., Baliga-Rao, M. P., & Baliga, M. S. (2013). Hepatoprotective properties of the Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis Gaertn): a review.Food & function,4(10), 1431-1441.
- [3] Sato, R., Buesa, L. M., & Nerurkar, P. V. (2010). Anti-obesity effects of Emblica officinalis (Amla) are associated with inhibition of nuclear transcription factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ).
- [4] Bindhu, B., Swetha, A. S., & Veluraja, K. (2015). Studies on the effect of phyllanthus emblica extract on the growth of urinary type struvite crystals invitro.Clinical Phytoscience,1(1), 3.
- [5] Mirunalini, S., & Krishnaveni, M. (2010). Therapeutic potential of Phyllanthus emblica (amla): the ayurvedic wonder.Journal of basic and clinical physiology and pharmacology,21(1), 93-105.
- [6] Jacob, A., Pandey, M., Kapoor, S., & Saroja, R. (1988). Effect of the Amla (Indian Gooseberry) on serum cholesterol levels in men aged 35-55 years.European journal of clinical nutrition,42(11), 939-944.
- [7] Gopa, B., Bhatt, J., & Hemavathi, K. G. (2012). A comparative clinical study of hypolipidemic efficacy of Amla (Emblica officinalis) with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase inhibitor simvastatin.Indian journal of pharmacology,44(2), 238-242.
- [8] Al-Rehaily, A. J., Al-Howiriny, T. A., Al-Sohaibani, M. O., & Rafatullah, S. (2002). Gastroprotective effects of'Amla'Emblica officinalis on in vivo test models in rats.Phytomedicine,9(6), 515.
- [9] Uddin, M. S., Mamun, A. A., Hossain, M. S., Akter, F., Iqbal, M. A., & Asaduzzaman, M. (2016). Exploring the Effect ofPhyllanthus emblicaL. on Cognitive Performance, Brain Antioxidant Markers and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Rats: Promising Natural Gift for the Mitigation of Alzheimer's Disease.Annals of neurosciences,23(4), 218-229.
- [10] Mehmood, M. H., Rehman, A., Rehman, N. U., & Gilani, A. H. (2013). Studies on prokinetic, laxative and spasmodic activities of Phyllanthus emblica in experimental animals.Phytotherapy Research,27(7), 1054-1060.
- [11] Sancheti, G., Jindal, A., Kumari, R., & Goyal, P. K. (2005). Chemopreventive action of emblica officinalis on skin carcinogenesis in mice.Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP,6(2), 197-201.
- [12] Sumalatha, D. (2013). Antioxidant and Antitumor activity of Phyllanthus emblica in colon cancer cell lines.Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci,2, 189-195.
- [13] Ngamkitidechakul, C., Jaijoy, K., Hansakul, P., Soonthornchareonnon, N., & Sireeratawong, S. (2010). Antitumour effects of Phyllanthus emblica L.: induction of cancer cell apoptosis and inhibition of in vivo tumour promotion and in vitro invasion of human cancer cells.Phytotherapy research,24(9), 1405-1413.
- [14] Zhong, Z. G., Luo, X. F., Huang, J. L., Cui, W., Huang, D., Feng, Y. Q., ... & Huang, Z. Q. (2013). Study on the effect of extracts from the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica on immune function of mice.Zhong yao cai= Zhongyaocai= Journal of Chinese medicinal materials,36(3), 441-444.
- [15] Rao, T. P., Okamoto, T., Akita, N., Hayashi, T., Kato-Yasuda, N., & Suzuki, K. (2013). Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced procoagulant and pro-inflammatory factors in cultured vascular endothelial cells.British Journal of Nutrition,110(12), 2201-2206.
- [16] D'souza, J. J., D'souza, P. P., Fazal, F., Kumar, A., Bhat, H. P., & Baliga, M. S. (2014). Anti-diabetic effects of the Indian indigenous fruit Emblica officinalis Gaertn: active constituents and modes of action.Food & function,5(4), 635-644.
- [17] Variya, B. C., Bakrania, A. K., & Patel, S. S. (2016). Emblica officinalis (Amla): A review for its phytochemistry, ethnomedicinal uses and medicinal potentials with respect to molecular mechanisms.Pharmacological research,111, 180-200.
- [18] Fujii, T., Wakaizumi, M., Ikami, T., & Saito, M. (2008). Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) extract promotes procollagen production and inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts.Journal of Ethnopharmacology,119(1), 53-57.
- [19] Luanpitpong, S., Nimmannit, U., Pongrakhananon, V., & Chanvorachote, P. (2011). Emblica (Phyllanthus emblica Linn.) fruit extract promotes proliferation in dermal papilla cells of human hair follicle.Res J Med Plant,5, 95-100.
-
 healthYou Can Rely On Simple Indian Superfoods From Local Market To Counter Diabetes, What You Must Include In Diet!
healthYou Can Rely On Simple Indian Superfoods From Local Market To Counter Diabetes, What You Must Include In Diet! -
 healthWeight Loss: What Happens When You Drink Amla And Ginger Juice Once Every Week?
healthWeight Loss: What Happens When You Drink Amla And Ginger Juice Once Every Week? -
 healthWhat Happens If You Eat Too Much Amla (Indian Gooseberry)? How Much Is Too Much?
healthWhat Happens If You Eat Too Much Amla (Indian Gooseberry)? How Much Is Too Much? -
 beautyNatural Remedies For Hair Loss: Amla, Coconut Oil And Hibiscus; Try It Today!
beautyNatural Remedies For Hair Loss: Amla, Coconut Oil And Hibiscus; Try It Today! -
 beautyVisible Changes In A Week: Amla and Curry Leaves for Hair Loss
beautyVisible Changes In A Week: Amla and Curry Leaves for Hair Loss -
 beautyHair Loss Will Be Old News With This 100 Year-Old Hibiscus And Amla Oil Recipe
beautyHair Loss Will Be Old News With This 100 Year-Old Hibiscus And Amla Oil Recipe -
 beautyHair Fall: Try This Amla-Quinoa Hair Pack Every Week
beautyHair Fall: Try This Amla-Quinoa Hair Pack Every Week -
 skin careAmla For Winter Skincare: 3 Ways To Use It!
skin careAmla For Winter Skincare: 3 Ways To Use It! -
 skin careJanhvi Kapoor's Favourite Go-To DIY Ingredient: 3 Ways To Use It For Your Skin
skin careJanhvi Kapoor's Favourite Go-To DIY Ingredient: 3 Ways To Use It For Your Skin -
 diabetesIs Indian Gooseberry (Amla) Good For Diabetes?
diabetesIs Indian Gooseberry (Amla) Good For Diabetes? -
 hair careAmla: Benefits For Hair & How To Use
hair careAmla: Benefits For Hair & How To Use -
 skin careBenefits Of Amla For Skin And How To Use
skin careBenefits Of Amla For Skin And How To Use


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



