Just In
- 8 hrs ago

- 8 hrs ago

- 9 hrs ago

- 9 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Finance
 7:1 Bonus, 1:10 Split: At Rs 3.5, NBFC Penny Stock Hits Back-To-Back Lower Circuits; Big Announcement Soon
7:1 Bonus, 1:10 Split: At Rs 3.5, NBFC Penny Stock Hits Back-To-Back Lower Circuits; Big Announcement Soon - Movies
 EXCLUSIVE Interview! Alankrita Sahai On Journey From Beauty Pageant Winner To Films, Nepotism In Bollywood
EXCLUSIVE Interview! Alankrita Sahai On Journey From Beauty Pageant Winner To Films, Nepotism In Bollywood - News
 EVM VVPAT Vote Cross-Checking Case: Can't Count 60 Crore Slips: Supreme Court; Next Hearing On Thursday
EVM VVPAT Vote Cross-Checking Case: Can't Count 60 Crore Slips: Supreme Court; Next Hearing On Thursday - Sports
 KKR vs RR, IPL 2024 Twitter Reaction: Sunil Narine hailed by Social Media after Stellar Century
KKR vs RR, IPL 2024 Twitter Reaction: Sunil Narine hailed by Social Media after Stellar Century - Education
 UPSC CDS 1 Exam on 21 April 2024
UPSC CDS 1 Exam on 21 April 2024 - Automobiles
 Jeep Compass Gets More Powerful 268.3bhp Turbo Petrol Engine – Check Out All The Details Here
Jeep Compass Gets More Powerful 268.3bhp Turbo Petrol Engine – Check Out All The Details Here - Technology
 Redmi Pad SE With 90Hz Display Launching on April 23 in India; Could Be Priced for Less Than Rs 20,000
Redmi Pad SE With 90Hz Display Launching on April 23 in India; Could Be Priced for Less Than Rs 20,000 - Travel
 From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
From Coconut Breaking on Head to Men Dressing as Women: 12 Unique Indian Rituals Explored
Muscle Cramps: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis And Treatment
Muscle cramps are sudden involuntary contraction that occurs in one or more muscles. They can be often painful which may happen while exercising, resting or sleeping at night. Muscle cramps are common and usually are seen among the elderly and in young people after a vigorous workout [1].

What Are Muscle Cramps? [2]
A muscle cramp is characterised by a sudden, painful involuntary contraction of a single muscle, entire muscle group or selected muscle fibres. The muscles in the arms and legs are voluntary muscles, which means you can control their movement and they alternately contract and relax. The muscles in the neck, head and trunk work in the same way.
When a muscle or muscle fibre involuntarily contracts, it can lead to muscle cramps. Muscle cramps can last from few minutes to a few seconds depending on the cause.


Causes Of Muscle Cramps
• Exercise associated muscle cramp (EAMC) - It happens during or immediately after an exercise. Exercise associated muscle cramp occurs either due to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance or a transient peripheral neurological disorder. Excessive sweating due to strenuous exercise causes dehydration and loss of electrolytes (magnesium, calcium, potassium and sodium), which leads to muscle cramping [2].
On the other hand, repetitive muscle exercise can cause muscle fatigue which causes an increase in excitatory afferent activity within the muscle spindles and decreases inhibitory afferent activity within the Golgi tendon. All of this leads to altered neuromuscular activity.
• Diabetes - Muscle cramps in diabetic patients have been linked to the presence of neuropathy, with a hyper excitability of the peripheral nerve. Around 60 per cent of type 1 diabetic patients have less muscle cramps as compared to 80 per cent of type 2 diabetic patients. In type 2 diabetes, nephropathy causes muscle cramps [2].
• Nocturnal leg cramps - The exact cause of nocturnal leg cramps is unknown. However, it could be due to certain activities such as when a person stands a lot while working or performing high physical activities during the day. It could also be due to electrolyte imbalance, neurological disorders, hormonal and metabolic disorders or compressed nerve roots or arterial vessels [2].
In addition, consumption of diuretics, beta-blockers, and statins drugs could also be the cause of leg cramps at night. The cramps usually occur in the calf of the leg.
• Leg cramps in pregnant women - Muscle cramps are common in pregnant women and what exactly causes it is unknown. However, it could be due to many factors and these include alterations of neuromuscular function, weight gain, inadequate blood flow to the muscles, muscles of the lower limbs working more, or peripheral nerve compressions [2].
• Writer's cramp - It is a specific type of focal dystonia (involuntary muscle contraction causing repetitive or twisting movements) of the hands which can occur while doing any fine motor movements such as writing. It occurs in people aged between 30 to 50 years [2].
• Cramp-fasciculation syndrome(CFS) - It is a rare condition of the muscles which causes persistent muscle cramping and twitching [2].
• Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) - Muscle cramp is a common symptom of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a disease of the nervous system that weakens the muscles and disables physical functionality. 95 per cent of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis have reported muscle cramps [2].
• Cirrhosis - About 88 per cent of cirrhosis patients experience muscle cramps [2].
• Anti-Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein Antibody (Anti-MAG) Neuropathy - It is a rare disease that causes muscle cramps in 60 per cent of the patients with this condition [2].
• End-stage kidney disease - Patients with chronic kidney failure who are undergoing dialysis can experience muscle cramps due to low magnesium levels in the body [3].


Symptoms Of Muscle Cramps
The most obvious symptom of muscle cramp is a sudden, sharp pain that usually develops in the leg muscles, particularly in the calf. You might feel or see a firm, tender lump of swollen muscle beneath the skin.

Risk Factors Of Muscle Cramps
•
Age
•
Dehydration
•
Pregnancy
•
Medical
Conditions

When To See A Doctor
Muscle cramps usually go away on their own and are rarely serious to seek medical care. However, you should consult a doctor if you experience severe discomfort, swollen leg, redness in the skin, muscle weakness and when they don't improve with self-care.
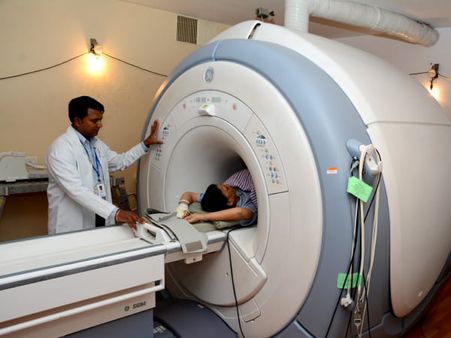
Diagnosis Of Muscle Cramps
The doctor will perform a physical examination and ask questions about the onset of muscle cramps. The doctor may conduct an electromyography (EMG), a diagnostic procedure to check the health of the muscles and the nerve cells that control the motor neurons. Other tests such as MRI or CT scan can rule out any neurological lesions [4].
Treatment Of Muscle Cramps
Self-care measures can treat muscle cramps. In addition, your doctor can show some stretching exercises that can help relax the muscles [4]. And muscle relaxant medications may be prescribed by your doctor to ease muscle cramps if caused by an injury.

Prevention Of Muscle Cramps
•
Do
warm-up
exercises
before
starting
any
exercise
as
it
will
help
reduce
the
muscle
strain.
•
Avoid
exercising
immediately
after
eating
meals.
•
Reduce
the
intake
of
caffeinated
beverages
•
Drink
plenty
of
water
to
prevent
dehydration.
•
Eat
calcium
and
potassium-rich
foods.
Common FAQs
Q. How do you get rid of muscle cramps fast?
A. Stretch and massage the cramped muscle and apply cold or warm water compress on the affected muscles.
Q. What is the best vitamin for leg cramps?
A. Increase the intake of magnesium to reduce the risk of muscle cramps.
Q. What is the best natural muscle relaxer?
A. Chamomile, cherry juice, magnesium, vitamin D, cayenne pepper and blueberry smoothies are some of the best natural muscle relaxers.
Q. How can I stop my legs from cramping at night?
A. Stretch your legs, drink plenty of water, change your sleeping position, avoid sleeping on a heavy bedding and wear the right footwear.
-
 disorders cureHeat Cramps: Is It A Serious Condition? Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Treatments And Prevention
disorders cureHeat Cramps: Is It A Serious Condition? Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Treatments And Prevention -
 pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread?
pregnancy parentingWhite Lung Syndrome: What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease Rampant In China? How Does It Spread? -
 healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
healthWorld HIV/AIDS Day: What Is The Difference Between HIV and AIDS? -
 healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDengue 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More
healthDiarrhoea 101: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Complications, Treatment, Prevention, Diet And More -
 health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy
health'Epileptic Nightmare' of Neurocysticercosis: The Hidden Epidemic of Parasites Causing Epilepsy -
 pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby
pregnancy parentingLife-Threatening Risk During Pregnancy: Sepsis Can Harm Both Mother and Baby -
 healthStay Informed: The Hidden Dangers of Legionnaires' Disease and How to Prevent It
healthStay Informed: The Hidden Dangers of Legionnaires' Disease and How to Prevent It -
 healthMyths vs Facts: Can A Single Mosquito Bite Really Give You Dengue?
healthMyths vs Facts: Can A Single Mosquito Bite Really Give You Dengue? -
 healthTop 5 Reasons For Vaginal Rash: When You Should See A Doctor
healthTop 5 Reasons For Vaginal Rash: When You Should See A Doctor -
 healthCan Inhaling Menthol Help Improve Memory For Alzheimer's Disease?
healthCan Inhaling Menthol Help Improve Memory For Alzheimer's Disease? -
 healthWorld Vitiligo Day 2023: Are You At Risk Of Developing Vitiligo?
healthWorld Vitiligo Day 2023: Are You At Risk Of Developing Vitiligo?


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications




