Just In
- 1 hr ago

- 11 hrs ago

- 12 hrs ago

- 16 hrs ago

Don't Miss
- Finance
 Indian Railway Finance Corp IRFC: Top NBFC Railway Stock Advised To BUY; Short-To-Long Term Target Prices
Indian Railway Finance Corp IRFC: Top NBFC Railway Stock Advised To BUY; Short-To-Long Term Target Prices - Sports
 Most Sixes in IPL 2024 After CSK vs LSG Match: Top 10 Players And Teams To Hit Most Sixes As Of April 24
Most Sixes in IPL 2024 After CSK vs LSG Match: Top 10 Players And Teams To Hit Most Sixes As Of April 24 - Technology
 Apple Confirms Special Event for May 7: iPad Air, iPad Pro 2024 Models Expected
Apple Confirms Special Event for May 7: iPad Air, iPad Pro 2024 Models Expected - News
 Senator Lambie Calls For Elon Musk's Imprisonment Over Wakeley Church Stabbing Posts
Senator Lambie Calls For Elon Musk's Imprisonment Over Wakeley Church Stabbing Posts - Movies
 Mirzapur 3 OTT Release Date, Platform: When Will Mirzapur Season 3 Premiere On Amazon Prime Video?
Mirzapur 3 OTT Release Date, Platform: When Will Mirzapur Season 3 Premiere On Amazon Prime Video? - Education
 Telangana Inter Manabadi 1st and 2nd Year Results 2024 to be Declared Tomorrow
Telangana Inter Manabadi 1st and 2nd Year Results 2024 to be Declared Tomorrow - Automobiles
 Chrysler Pacifica Marks Seven Years As Most Awarded Minivan With New Campaign
Chrysler Pacifica Marks Seven Years As Most Awarded Minivan With New Campaign - Travel
Kurnool's Hidden Gems: A Guide To Exploring India's Lesser-Known Treasures
World Tuberculosis Day 2021: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Of Tuberculosis
Every year, World Tuberculosis (TB) Day is observed on March 24 to raise public awareness about the health, social and economic consequences of TB and to bring efforts to end TB globally. The theme of World TB Day 2020 is 'The Clock is Ticking'.

According to the World Health Organisation, tuberculosis is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. In 2018, 10,000,000 people fell ill and 1,500,000 died from tuberculosis. Every day, over 4000 people lose their lives to TB and close to 30,000 people fall ill.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. It is caused by bacteria that get easily transmitted from person to person through coughs and sneezes.
What Is Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads through the air from person to person through sneezing, coughing, laughing, speaking or spitting. People infected with this bacteria have a 5 to 15 per cent lifetime risk of falling ill with this disease [1].

Types of tuberculosis
• Latent TB infection - In this type of TB, the bacteria is inside the body, but in an inactive state which doesn't make you fall sick and there are no symptoms. The body is able to fight the bacteria to inhibit growth and prevent it from spreading. However, treatment is required for latent TB infection, so that the bacteria don't become active [2] . People with active TB who have received proper treatment for at least 2 weeks aren't contagious.
• Active TB disease - If the bacteria become active in latent TB infection the next stage is TB disease. In this case, you fall sick and the disease spreads to others. The symptoms of TB disease include pain in the chest, a bad cough that lasts longer than 3 weeks, and coughing up blood.
• Miliary TB - It is a rare form of TB disease that occurs when the bacteria enter the bloodstream. After which, it starts spreading quickly all over the body in tiny nodules and affects the organs [3] .
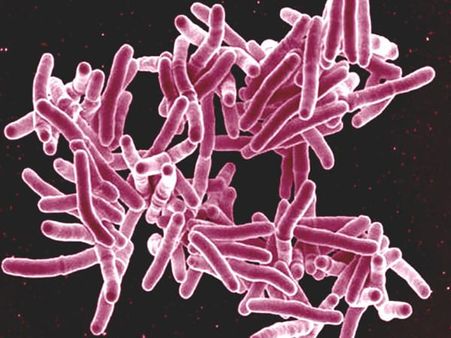
What Causes Tuberculosis
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread through microscopic droplets released into the air by a person. Tuberculosis is contagious and the chances of getting it from another person are higher when you are in close proximity.
The drug-resistant bacteria strains develop when antibiotic medicines fail to kill the bacteria. The Multi-drug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) arises when the surviving bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics such as rifampin and isoniazid.
The HIV virus which causes AIDS suppresses your immunity, making it difficult for the body to control the TB bacteria. This is why most people with HIV are much more likely to get tuberculosis [4] .

What Are The Symptoms Of Tuberculosis
•
Feeling
sick
and
weak
•
Cough
lasting
for
more
than
3
weeks
•
Fever,
chills
and
night
sweats
•
Chest
pain
•
Loss
of
appetite
•
Weight
loss
When TB spreads to other parts of the body the symptoms include the following:
•
Spinal
and
joint
pain
•
Meningitis
•
Improper
function
of
the
heart,
liver
and
kidneys
What Are The Risk Factors
•
Smoking
and
ingesting
tobacco-related
products
[5]
•
Diabetes
[6]
•
HIV/AIDS
•
Malnutrition
[7]
•
Kidney
disease
[8]
•
Certain
cancers
[9]
•
Some
drugs
to
treat
rheumatoid
arthritis,
psoriasis,
Crohn's
disease
•
Travelling
to
countries
like
Africa,
Asia,
Eastern
Europe,
Latin
America,
Russia,
and
the
Caribbean
Islands
where
tuberculosis
is
common
[10]
,
[11]
•
Poverty
and
substance
abuse
•
People
who
have
spent
time
with
someone
having
TB
disease
•
Health
care
workers
who
look
after
TB
patients
[12]
•
Children
and
adolescent
in
contact
with
adults
who
have
TB

When To See A Doctor
Consult a doctor if you experience high fever, sudden weight loss, night sweats and persistent cough. The doctor will then conduct some tests to find out the cause.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, people who have HIV/AIDS, are in contact with infected people, use IV drugs, are from countries where TB are common should see a doctor.

Diagnosis Of Tuberculosis
A doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to the sounds of your lungs while you breathe and check for swelling in the lymph nodes. The most common diagnostic test for tuberculosis is a skin test where a small substance called PPD tuberculin, an extract of the TB bacterium is injected in the inside of the forearm.
The doctor will check your arm after 24 to 48 hours to see if there is any swelling in the area. If the area has a red, swollen bump it means you have contracted TB. But, the skin test isn't absolutely accurate in few cases when people with AIDS don't respond to the TB skin test and if you have been vaccinated recently with the Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
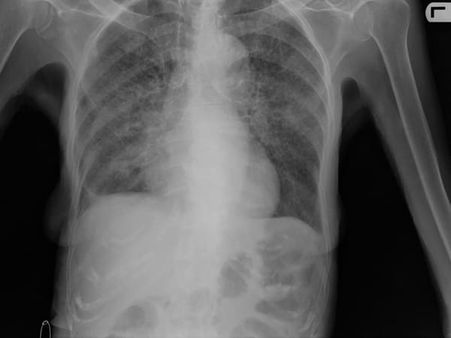
If your skin test result is positive, your doctor will conduct a chest X-ray or a CT scan. It will show the changes in the lungs caused by active TB. If the chest X-ray result is positive, your doctor will take samples of your sputum (mucus from your cough) to check for TB bacteria.
Blood tests are also done to confirm tuberculosis.
Treatment For Tuberculosis
The right medications can cure tuberculosis - which are mostly antibiotics. The antibiotic treatment depends on a person's age, overall health, possible resistance to drugs, TB bacteria is latent or active, and the location of the TB infection.
If you have latent TB, an individual needs to take one or two types of TB drugs. And if you have active TB, several antibiotics like rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol are taken for at least six to nine months.
A new 2019 study shows that researchers have been exploring shorter, more effective and safer treatments for patients who have drug-resistant TB. The treatment duration is shorter from 9 to 11 months and is as effective as drug-resistant TB treatment [13]
TB
medicines
can
be
harmful
to
the
liver
and
cause
various
side
effects
as
well
like
fever,
jaundice,
dark
urine,
nausea
and
vomiting,
and
loss
of
appetite.
The
treatment
course
should
be
completed
fully
to
cure
the
disease.
Because
any
bacteria
that
have
survived
during
the
treatment
could
become
resistant
to
antibiotic
drugs
and
could
lead
to
developing
MDR-TB
in
the
future.
A
directly
observed
therapy
(DOT)
is
recommended
to
stick
to
your
treatment
program.
Prevention Of Tuberculosis
•
During
the
first
few
weeks
of
treatment,
don't
step
outside
and
avoid
contact
with
other
people
to
minimize
the
risk
of
transmission
of
germs.
•
Cover
your
mouth
while
you
sneeze
and
cough
and
ventilate
the
room
as
germs
spread
easily
in
closed
spaces.
•
In
some
countries,
children
are
given
BCG
injections
for
vaccination.
-
 healthWorld Tuberculosis Day: Is Tuberculosis Contagious? How To Reduce TB Risk?
healthWorld Tuberculosis Day: Is Tuberculosis Contagious? How To Reduce TB Risk? -
 healthWorld Tuberculosis Day: Types Of Tuberculosis
healthWorld Tuberculosis Day: Types Of Tuberculosis -
 wellnessCentury-Old TB Vaccine Could Be Effective Against Covid-19 And Other Infections: New Study
wellnessCentury-Old TB Vaccine Could Be Effective Against Covid-19 And Other Infections: New Study -
 wellnessTB Patients At Increased Risk Of All-Cause Mortality Even After Treatment: ICMR
wellnessTB Patients At Increased Risk Of All-Cause Mortality Even After Treatment: ICMR -
 wellnessNational Institute For Research In Tuberculosis Developing Sputum-Free Tests For Diagnosing TB
wellnessNational Institute For Research In Tuberculosis Developing Sputum-Free Tests For Diagnosing TB -
 wellnessGovt To Launch Programme For Adopting, Providing Nutritional, Treatment Support To TB Patients
wellnessGovt To Launch Programme For Adopting, Providing Nutritional, Treatment Support To TB Patients -
 wellnessSerum Institute Seeks Emergency Use Authorisation For Its rBCG Tuberculosis Vaccine
wellnessSerum Institute Seeks Emergency Use Authorisation For Its rBCG Tuberculosis Vaccine -
 wellnessWorld TB Day 2022: How Does Tuberculosis Affect Fertility? (Expert Article)
wellnessWorld TB Day 2022: How Does Tuberculosis Affect Fertility? (Expert Article) -
 babyWorld TB Day 2022: Tuberculosis In Babies And Children, Its Stages, Symptoms And Can It Be Prevented?
babyWorld TB Day 2022: Tuberculosis In Babies And Children, Its Stages, Symptoms And Can It Be Prevented? -
 disorders cureWorld TB Day 2022: FAQs On Tuberculosis Treatment And Its Link To COVID-19
disorders cureWorld TB Day 2022: FAQs On Tuberculosis Treatment And Its Link To COVID-19 -
 disorders cureWorld TB Day: Expert Article On Tuberculosis And Ayurveda
disorders cureWorld TB Day: Expert Article On Tuberculosis And Ayurveda -
 nutritionWorld TB Day 2022: Foods To Consume And Avoid By Tuberculosis Patients
nutritionWorld TB Day 2022: Foods To Consume And Avoid By Tuberculosis Patients


 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications



